Malay language facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Malay |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bahasa Melayu بهاس ملايو |
||||
| Native to | Indonesia (as Indonesian) Malaysia (as Malaysian) |
|||
| Native speakers | 77 million (2007) Total: more than 215 million |
|||
| Language family |
Austronesian
|
|||
| Standard forms | ||||
| Writing system | Latin (Malay alphabet) Arabic (Jawi) Thai (in Thailand) Historically Pallava, Kawi, Rencong |
|||
| Official status | ||||
| Official language in | Indonesia Malaysia Brunei Singapore Cocos (Keeling) Islands (de jure) |
|||
| Recognised minority language in | Indonesia (Local Malay enjoys the status of a regional language in Sumatra apart from the national standard of Indonesian) | |||
| Regulated by | Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka (Institute of Language and Literature); Majlis Bahasa Brunei–Indonesia–Malaysia (Brunei–Indonesia–Malaysia Language Council – MABBIM) (a trilateral joint-venture) |
|||
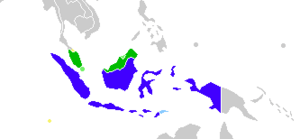
Malaysia
Indonesia Singapore and Brunei, where Standard Malay is an official language East Timor, where Indonesian is a working language Southern Thailand and the Cocos Isl., where other varieties of Malay are spoken |
||||
|
||||
The Malay language, also known as Bahasa Melayu, is a language spoken by many people. It belongs to the Austronesian family of languages. You can hear it in countries like Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore. It is also spoken in parts of Southern Thailand.
Malay is the native language for people living near the Strait of Malacca. This includes the coasts of the Malay Peninsula in Malaysia and the eastern coast of Sumatra in Indonesia. It is also spoken in parts of Borneo, like western coastal Sarawak and West Kalimantan. Malay is also used for trade in the southern Philippines. This includes areas like the Zamboanga Peninsula and the Sulu Archipelago.
Contents
Malay and Indonesian: Are They the Same?
Malay is a very diverse language. It has many different versions, creoles, and dialects.
Different Names for Malay
In Indonesia, the language is called Bahasa Indonesia. This means "Indonesian language". It is based on a specific dialect called Riau-Johor. In Malaysia, it is known as Bahasa Malaysia, or "Malaysian". In Singapore, Brunei, and Thailand, it is called Bahasa Melayu, meaning "Malay language".
Bahasa Malaysia and Bahasa Melayu are very similar. They come from the same dialect. However, Bahasa Indonesia has some differences. For example, it has words that sound similar but mean different things. These are called false friends. Even so, about 80% of words in Indonesian and Malaysian are cognates. This means they come from the same origin.
Malay in Different Regions
In southern Thailand, people speak Bahasa Melayu. They also have their own special dialect called Yawi, or "Bahasa Jawi". Brunei's national language is Bahasa Melayu. But Bruneians also speak their own dialect, called Brunei Melayu.
People in Indonesia usually see Indonesian and Malaysian/Malay as separate languages. They prefer Bahasa Indonesia to be called by its own name. In Indonesia, Malay is considered a local language. Bahasa Indonesia is the national language. Malays in Indonesia learn their local Malay dialects first. Malaysians, however, often see the two as the same language.
How Malay is Written
Malay is usually written using the Latin alphabet. This writing system is called Rumi. There is also another way to write Malay using a changed Arabic alphabet. This is called Jawi.
Official Writing Systems
Rumi is the official writing system in Malaysia and Singapore. The Indonesian language also uses the Latin script, but it has its own official spelling rules. Both Rumi and Jawi are official in Brunei.
Keeping Jawi Alive
There are efforts to keep the Jawi script alive. People want to encourage Malays in Malaysia to use it more. Students taking Malay language exams in Malaysia can choose to answer questions using Jawi script. However, the Latin alphabet (Rumi) is still the most common way to write Malay in Malaysia. People use it for both official documents and everyday notes.
Old Ways of Writing Malay
In the past, Malay was written using different scripts. Before the Arabic script arrived, people used Pallava, Kawi, and Rencong scripts. Some of these old scripts are still used today by the Champa Malay people in Vietnam and Cambodia.
Images for kids
-
The Kedukan Bukit Inscription, written using the Pallava alphabet. It is the oldest example of the Old Malay language found in South Sumatra, Indonesia.
-
Malay road signs in Jakarta, Indonesia. The blue sign means "Lane for dropping passengers only". The small no-parking sign means "until next sign" in Indonesian.
See also
 In Spanish: Idioma malayo para niños
In Spanish: Idioma malayo para niños






