Boolean algebra facts for kids
In mathematics and computer science, Boolean algebra is a special kind of algebra. It's different from the math you usually do with numbers.
In Boolean algebra, variables don't stand for numbers. Instead, they stand for truth values: true or false. These are often shown as 1 (for true) and 0 (for false).
Boolean algebra also uses special operators like AND, OR, and NOT. These are used to combine or change true/false statements. Think of it as a formal way to describe how logic works, just like regular algebra describes how numbers work.
George Boole first introduced these ideas in his books in the mid-1800s. Later, in the 1930s, Claude Shannon showed how Boolean algebra could be used to design electronic circuits. This was a huge step! Today, Boolean algebra is key to how all modern computers and programming languages work. It's also used in other areas like set theory.
Contents
History of Boolean Algebra
Long before George Boole, a scientist named Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz had similar ideas about an "algebra of concepts." He thought about using binary (0s and 1s) to represent ideas, which was a bit like what Boolean algebra would become.
George Boole created his system in the mid-1800s. His work helped start the fields of abstract algebra and mathematical logic. Other mathematicians like William Stanley Jevons and Ernst Schröder later improved and expanded Boole's ideas. They helped make it the formal mathematical system we know today.
A big moment came in the 1930s. A brilliant engineer named Claude Shannon realized that Boole's rules could be used for switching circuits. These are the circuits that turn things on and off in computers. Shannon showed how to use Boolean algebra to design and understand these circuits. This is why "switching algebra" and "Boolean algebra" are often used to mean the same thing in computer design.
Today, Boolean algebra helps engineers design very complex computer chips. It helps them make sure the circuits work correctly and efficiently.
Understanding Boolean Values
In regular algebra, variables represent numbers like 1, 2, or 100. In Boolean algebra, variables only represent two values: false (0) or true (1).
It's important to remember that these 0s and 1s are not like the numbers you add or multiply in everyday math. For example, in Boolean algebra, 1 + 1 does not equal 2. Instead, it might equal 1 (if we're talking about OR logic) or 0 (if we're talking about XOR logic).
Boolean algebra can also work with functions that give back true or false values. For example, a bit vector (a sequence of 0s and 1s) is a common way to use these functions. Think of it like a list of switches, each either on (1) or off (0).
Basic Boolean Operations
Regular algebra has operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Boolean algebra has three main operations:
- AND (also called conjunction)
- OR (also called disjunction)
- NOT (also called negation)
These operations work on Boolean variables, which can only be 0 (false) or 1 (true).
How AND, OR, and NOT Work
Let's look at how these operations work with two variables, x and y.
| Logical Operation | Operator | What it means | When is it True (1)? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conjunction | AND | x ∧ y | Only if both x and y are 1 (true). Otherwise, it's 0 (false). |
| Disjunction | OR | x ∨ y | If either x or y (or both) are 1 (true). Only 0 (false) if both are 0. |
| Negation | NOT | ¬x | If x is 0 (false), then ¬x is 1 (true). If x is 1 (true), then ¬x is 0 (false). It flips the value. |
We can also show these operations using truth tables. These tables list all possible inputs and their results.
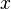 |
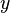 |
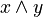 (AND) (AND) |
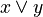 (OR) (OR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
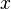 |
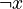 (NOT) (NOT) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Just like in regular math, you evaluate parts of an expression in parentheses first.
You can actually define AND using NOT and OR, and OR using NOT and AND. These are called De Morgan's laws:
- x AND y = NOT ( (NOT x) OR (NOT y) )
- x OR y = NOT ( (NOT x) AND (NOT y) )
Where is Boolean Algebra Used?
Boolean algebra is super important for computers, logic, and other math areas like set theory.
Computers and Digital Logic
In the early 1900s, engineers realized that Boolean algebra was perfect for describing how electrical circuits work. Claude Shannon proved this formally in 1937.
Today, every modern computer uses two-value Boolean logic. This means their circuits are built to represent true (1) and false (0). They do this in different ways, like using high or low voltages on wires. It's much easier for computers to tell the difference between two states (on/off) than many states (like 0, 1, 2, 3 volts).
When you program a computer, especially at a low level, you work with these 0s and 1s. Computers can do both math operations (like adding numbers) and logical operations (like ANDing two sequences of bits). Boolean algebra helps programmers understand and control how computers process information.
Two-Valued Logic in Everyday Life
The idea of having only two choices (true/false, yes/no) is very useful.
- In a court of law, questions are often framed to get a simple "guilty" or "not guilty" answer.
- In math, a statement is either "true" or "false." There's no "maybe."
- In set theory, an item is either "in" a set or "not in" a set.
This simple two-valued system makes things clear and easy to organize.
Sometimes, people extend this idea to "multi-valued logic" or "fuzzy logic". This is where values can be anywhere between 0 and 1, not just 0 or 1. It's like saying something is "partially true" or "mostly false." This is used in areas like artificial intelligence to deal with uncertainty.
Boolean Operations in Action
Boolean operations are used in many practical ways.
Natural Language (with caution!)
Words like "and," "or," and "not" are used in everyday language. Sometimes they mean the same as their logical counterparts. For example, "The sky is blue AND the grass is green" is true only if both parts are true.
However, natural language can be tricky. "Jim opened the door AND Jim walked through the door" usually means "Jim opened the door, AND THEN Jim walked through." The order matters, which is not always the case in pure Boolean logic. So, while there's a connection, Boolean algebra isn't perfect for understanding all natural language.
Digital Logic Gates
In digital logic, Boolean operations combine the bits (0s and 1s) carried on wires. These operations are performed by tiny electronic components called logic gates. For example, an AND gate will only output a 1 if both of its inputs are 1.
Search Engines
When you search online, you're often using Boolean logic without realizing it!
- If you type "dogs cats" into a search engine, it usually means "dogs AND cats." It will look for pages that have both words.
- If you type "dogs OR cats," it will find pages that have either "dogs" or "cats" (or both).
- If you type "dogs -cats," it means "dogs AND NOT cats." It will find pages about dogs but exclude any that also mention cats.
Computer Graphics and Design
Boolean operations are used in computer displays and computer aided design (CAD) software.
- In computer graphics, they help combine different parts of an image. For example, you can use Boolean operations to decide how a new image should blend with an existing one on your screen.
- In CAD, designers can build complex 3D objects by combining simpler shapes using Boolean operations. For example, to make a hole in a block, you can use the "block AND NOT cylinder" operation. This subtracts the cylinder shape from the block.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Álgebra de Boole para niños
In Spanish: Álgebra de Boole para niños

