Buenos Aires National Wildlife Refuge facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Buenos Aires National Wildlife Refuge |
|
|---|---|
|
IUCN Category IV (Habitat/Species Management Area)
|
|

A view in the refuge
|
|
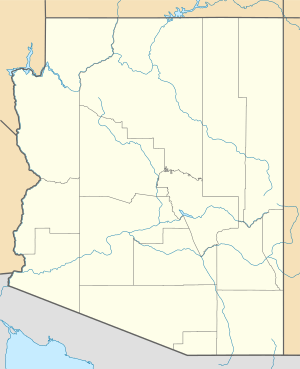
| Location | Pima County, Arizona, United States |
| Nearest city | Arivaca, Arizona |
| Area | 117,107 acres (473.92 km2) |
| Established | 1985 |
| Governing body | U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service |
The Buenos Aires National Wildlife Refuge (often called Buenos Aires NWR) is a huge protected area in Pima County, Arizona, United States. It covers about 117,107 acres (which is about 47,391 hectares or 474 square kilometers!). This special place was created in 1985. Its main job is to protect homes, called habitats, for many plants and animals. Some of these animals are even rare or endangered, meaning they need extra help to survive.
Nature's Home
This refuge is mostly made up of a special type of grassland called a semidesert grassland. It's a perfect home for animals like the masked bobwhite quail and pronghorn. These animals are being brought back to the area to help their populations grow.
Fires, both natural and controlled by people, are very important here. They help keep the grasslands healthy and restore the wide-open "sea of grass" that used to cover the Altar Valley.
There are also wet areas, called riparian areas or wetlands, along Arivaca Cienega and Arivaca Creek. These watery spots are like magnets for many different kinds of birds. To the west of Arivaca Creek, you'll find Brown Canyon. It's tucked away in the Baboquivari Mountains. Here, a stream lined with sycamore trees winds through a forest of oak trees.
Amazing Animals
The Buenos Aires National Wildlife Refuge is bursting with wildlife! It's home to 58 different kinds of mammals. Some of the larger animals you might find are mule deer, white-tailed deer, pronghorn, javelina (which look a bit like wild pigs), and pumas (also known as cougars).
The refuge is also a paradise for birdwatchers, with more than 325 different bird species flying around. Plus, there are 53 types of reptiles and amphibians, like snakes, lizards, frogs, and toads.
Jaguars in the Refuge
The refuge is close to Mexico, and sometimes jaguars cross the border into the area. These big cats are very rare in the United States.
Between 2004 and 2007, scientists studied an older male jaguar in the refuge. They called him 'Macho B'. He had been seen and photographed in the area as early as 1996. During the study, he roamed across the mountains on both sides of the Altar Valley, which is inside the refuge. Scientists also found signs of at least one other jaguar in the area during that time.
Sadly, Macho B passed away. He was a very old jaguar, about 16 years old.
Images for kids