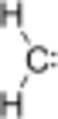Carbene facts for kids
A carbene is a special type of molecule that has a carbon atom at its center. This carbon atom has two bonds to other atoms and also two electrons that are not part of any bonds. Because this carbon atom only has six electrons around it (instead of the usual eight), carbenes are very reactive and like to join with other molecules.
Contents
Types of Carbenes: Singlet and Triplet
Carbenes can exist in two main forms: singlet or triplet. The difference between them is how their two unbonded electrons behave.
- In a singlet carbene, the two unbonded electrons act like a lone pair. This means they both stay in the same atomic orbital (a region around the atom where electrons are likely to be found).
- In a triplet carbene, the two unbonded electrons are in different orbitals. They also have the same spin, which is a property of electrons.
How Carbenes React
Carbenes are very versatile in how they react. They can act as both electrophiles (which means they are attracted to areas with lots of electrons) and nucleophiles (which means they have extra electrons they can share).
They are especially good at doing addition reactions. This is where they add themselves across double bonds in other molecules. They are also important in reactions called cheletropic reactions.
Are Carbenes Stable?
Most carbenes are very unstable and only exist for a very short time before reacting with something else. However, some special carbenes can be made to last for a longer period.
A famous example of a carbene that is more stable is found in Grubbs' catalyst. This important chemical was developed by a scientist named Robert Grubbs. Catalysts like this help chemical reactions happen faster and are used in many areas, including making new medicines and materials.
See also
 In Spanish: Carbeno para niños
In Spanish: Carbeno para niños
Images for kids