Addition reaction facts for kids
An addition reaction is a cool type of chemical reaction where two or more molecules join together to form a single, larger molecule. Think of it like two LEGO bricks clicking together to make a bigger structure!
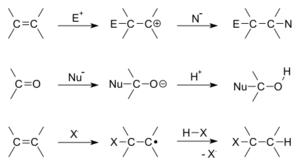
This kind of reaction usually happens when one of the molecules has a special connection between its atoms called a double bond or a triple bond. These bonds are like extra strong "hands" that can grab onto other atoms. These special bonds can be between carbon atoms, or even between carbon and oxygen or carbon and nitrogen atoms.
In an addition reaction, one molecule, called the nucleophile, has extra electrons it's ready to share. The other molecule, called the electrophile, is looking for electrons. When they meet, the nucleophile shares its electrons with the electrophile, forming a brand new connection and creating one bigger molecule.
Addition reactions are the opposite of elimination reactions, where a single molecule breaks apart into two or more smaller ones.
How Addition Reactions Work
Imagine a molecule with a double bond. This bond is like having two "hooks" connecting two atoms. In an addition reaction, one of these hooks can break open to allow new atoms or groups of atoms to attach.
The Key Players
- Nucleophile: This molecule is "electron-rich." It has electrons it wants to give away or share to form a new bond. Think of it as the "giver."
- Electrophile: This molecule is "electron-poor." It's looking for electrons to complete its own bonds. Think of it as the "taker."
When the nucleophile and electrophile meet, the electrons from the nucleophile move to form a new bond with the electrophile. This breaks the double or triple bond in the original molecule, and the new atoms or groups are "added" on.
Examples of Addition Reactions
Addition reactions are very common in chemistry and happen all around us.
- Adding Water: One simple example is when water (H2O) adds across a double bond. For instance, water can add to a molecule like ethene (a gas) to form ethanol (a type of alcohol).
- Joining at Carbonyls: Another common type involves molecules adding to a "carbonyl" group. A carbonyl group is a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom. Many important reactions in living things and in industries use this type of addition.
See also
 In Spanish: Reacción de adición para niños
In Spanish: Reacción de adición para niños