Cell growth facts for kids
Cell growth is all about how cells increase in number. It's like when a single parent cell gets ready and then splits into two or more new cells. This process is called cell division. Before a cell divides, it goes through a special preparation stage called interphase. During this time, the cell is very busy making new things and getting ready, even if you can't see big changes happening.
Contents
Stages of Cell Growth
Cells go through different stages to prepare for division. Think of it like a checklist before a big event!
- First Growth Phase (G1)
* In this stage, the cell grows bigger. * It also makes new parts called organelles. These are like tiny organs for the cell. * Examples include mitochondria (which make energy) and chloroplasts (in plant cells, which help with food). * The cell also checks to make sure everything is ready for the next big step: copying its DNA.
- Synthesis Phase (S)
* This is a super important stage! * The cell makes an exact copy of all its DNA molecules. * DNA is like the cell's instruction manual.
- Second Growth Phase (G2)
* The cell continues to grow even more. * It stores up extra energy. * This stage makes sure the cell is at its maximum size and has enough power for the upcoming division.
How Cell Numbers Grow
Cell numbers grow in a special way called "doubling." This means that with each new generation of cells, the number of cells should become twice as many as before. So, one cell becomes two, two cells become four, and so on!
How Cells Reproduce
Cells reproduce in a simple way called asexual reproduction. This means one parent cell can make new cells all by itself, without needing another cell.
The process of cell reproduction has three main parts:
- First, the parent cell makes a copy of its DNA.
- Second, the copied DNA is carefully separated into two equal groups of chromosomes. Chromosomes are structures that hold the DNA.
- Third, the entire cell physically divides into two new cells. This final step is usually called cytokinesis.
Cell reproduction is a bit different depending on the type of cell:
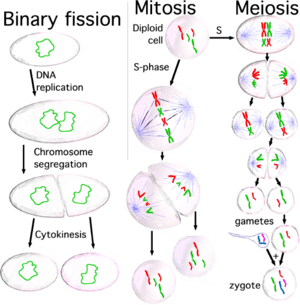
- Simple Cells (Prokaryotes): Cells like bacteria are called prokaryotes. They reproduce using a process called binary fission. This is a simple way of dividing that includes copying DNA, separating chromosomes, and then splitting the cell.
- Complex Cells (Eukaryotes): Cells in plants, animals, and fungi are called eukaryotes. Their reproduction is more complex. They use either mitosis or meiosis. Mitosis and meiosis are sometimes called "nuclear division" processes because they involve the nucleus of the cell.
Comparing Cell Reproduction Types
Before a cell starts to reproduce, its DNA content is copied. Let's say a cell has an amount of DNA we call Z. After the DNA is copied, the cell will have 2Z (double the amount) of DNA.
- Binary Fission and Mitosis: In these processes, the copied DNA is split equally into two new daughter cells. After the DNA is separated, the parent cell physically splits apart.
- Meiosis: This process is different because it involves two cell division steps. These two steps work together to create four daughter cells.
Let's look at human cells as an example:
- A human cell normally has 46 chromosomes.
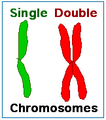
- After DNA is copied, a human cell will have 46 "double chromosomes." Each double chromosome has two copies of its DNA.
- During mitosis, these double chromosomes split. This creates 92 "single chromosomes." Half of these (46 single chromosomes) go into each of the two daughter cells.
- During meiosis, there are two steps where chromosomes separate. This makes sure that each of the four daughter cells gets one copy of each of the 23 types of chromosomes.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Crecimiento celular para niños
In Spanish: Crecimiento celular para niños