Developmental biology facts for kids
Developmental biology is a super cool science that studies how living things grow and change from a tiny beginning into a full-grown plant or animal. It looks at how a single cell, like a fertilized egg, becomes a complex organism with many different parts.
Scientists in this field explore how our genes control things like cell growth (how cells get bigger and multiply), differentiation (how cells become specialized, like a muscle cell or a nerve cell), and morphogenesis (how an organism gets its shape and structure). These amazing processes are what turn a single zygote (a fertilized egg) into a complete adult animal.
Contents
How Do Cells Become Different?
Differentiation is the process where cells change from being general to becoming specific types. Think of it like a team of builders: at first, they are all just builders, but then some become plumbers, some become electricians, and some become roofers.
All the cells in your body start from one original cell, the zygote. Over time, these cells become different types, like nerve cells, skin cells, or bone cells. This happens because certain genes in each cell are turned on or off, giving the cell its special job.
How Do Embryos Develop?
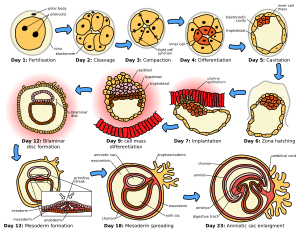
Embryogenesis is the first big step in the life cycle after fertilization. It's all about how an embryo develops from that first zygote.
Even though all living things start small, the way their embryos develop can be very different. For example, a human embryo develops differently from a fish embryo, especially when they belong to different major groups of animals.
How Do Organisms Grow?
Growth is simply when a body part or a whole organism gets bigger. This doesn't stop after the embryo stage! Growth happens in a few ways:
- Cell division: Cells make copies of themselves.
- Enlargement of cells: Cells themselves get bigger.
- Accumulation of material: Extra stuff builds up outside the cells.
In plants, growth can make the adult look very different from the tiny plant embryo. Special cells called stem cells are often responsible for growth because they can divide and then turn into many different cell types.
In some parts of the body, like the growth plates in our bones, dividing cells are found in specific areas. But some stem cells can even move to where they are needed, like from your bone marrow to help form new muscle or bone tissue.
What is Metamorphosis?

Many animals, like frogs and butterflies, have a larval stage. This is a young form of the animal that looks very different from the adult. For example, a caterpillar is the larval stage of a butterfly. It's great at eating and growing!
Then, something amazing happens called metamorphosis. The larva suddenly changes into an adult. A caterpillar, after growing enough, turns into an immobile pupa (like a chrysalis). Inside the pupa, the adult butterfly (called an imago) develops. Adult butterflies are specialized for flying and having babies, not for eating leaves like caterpillars!
Can Body Parts Grow Back?
Regeneration is when development is "reactivated" to grow back a missing body part. It's like your body hitting a rewind button for a specific area.
Scientists have studied this a lot in salamanders. These amazing creatures can grow back a whole limb if it gets cut off! Researchers hope that one day we might be able to help humans regenerate body parts too.
Humans don't have much natural regeneration as adults, but our liver is a cool exception. It can actually grow back a large part of itself if it's damaged. Just like in salamanders, liver regeneration involves some cells going back to an earlier, more flexible state.
Related topics
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Biología del desarrollo para niños
In Spanish: Biología del desarrollo para niños