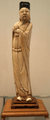Chinese mythology facts for kids

Chinese Mythology is a collection of exciting stories, beliefs, and gods from Ancient China.
Myths in China are different depending on the culture. The most common stories come from the Han culture. Today, the Chinese government recognizes 56 different ethnic groups. Each of these groups has its own language and special myths.
Contents
How the World Began
Before Everything: Chaos
"Chaos" is a word used in many Chinese creation myths. It describes what existed before the Earth and sky were formed. Each myth has a unique way of explaining Chaos and what happened next.
Amazing Creation Stories
One popular creation myth says the universe started as a giant egg. Inside this "Cosmic Egg," a being named Pangu was born. Pangu grew 10 feet every day for 18,000 years!
When Pangu died, his body turned into different parts of the world we see. His right eye became the moon, and his left eye became the sun. People were created when the wind touched the tiny bugs on his skin. This story is from an old text called Historical Records of the Three Sovereign Divinities and the Five Gods.
Another creation myth features the goddess Nü Gua. She created ordinary people by dragging a cord through mud. But the rich and powerful people were made carefully from yellow clay, like an artist molding statues.
A different creation story takes place in a land called Hun-Tun, which means "Center" or "Chaos." This was where Hu, the emperor of the Northern Sea, met Shu, the emperor of the Southern Sea. Hun-Tun couldn't eat, see, hear, or breathe. To thank Hun-Tun for his kindness, Hu and Shu decided to give him the necessary holes for these things. After seven days, one for each hole, Hun-Tun died. The world began right after his death.
Important Religions
Three major religions greatly influenced the government and people of Ancient China.
Buddhism
Buddhism started in India. It teaches about rebirth, also known as reincarnation. This means beings are reborn into different forms based on what they learned in their past lives. To stop this endless cycle, one must reach Nirvana or enlightenment. Reaching Nirvana is the main goal for Buddhists.
Buddhism is thought to have brought the idea of hell to Taoism. In this concept, hell is a place where people complete tasks to make up for bad things they did in life.
Confucianism
In the philosophy of Confucianism, everyone should live a moral and kind life. It's important for each person to understand their role in society. This could be as a father, a ruler, or a wife.
Confucianism's way of life is quite different from Taoism. Confucianism believes that the right way to live can be understood and followed logically. Taoism, however, believes the true "way" can never be fully known. Still, both religions valued tradition and honoring the past, so they often existed peacefully together.
Taoism
Also known as Daoism, Taoism is a school of thought or a religion. Taoist priests were known for healing people. Because of this, Taoism is credited with advancements in medicine and alchemy.
The Dao, or "the way," is a central idea in Taoism. It existed before and after creation. The Dao cannot be seen or heard. For Taoists, the ultimate goal is to return to the Dao. It is seen as both the beginning and the end of everything.
Gods and Goddesses
Creators
- In some Chinese myths, Pangu is the first living being. He is also seen as the creator of everything on Earth.
- Nü Gua is the goddess who created humans in one famous creation myth.
- Animism is the belief that natural forces, like wind or rivers, can be seen as gods.
List of Gods and Goddesses
- Heng o is the Goddess of the moon.
- Cheng Huang is the God of walls and ditches.
- Chih Nii is the Goddess of spinners, weavers, and clouds.
- Chin Shu Pao is a Guardian God.
- Chu Jung is the God of fire and executions.
- Erh Lang is a shape-shifter who fights evil spirits.
- Feng Po Po is the Goddess of winds.
- Fu Hsi is the God of happiness.
- Hou Chi is the God of Harvest.
- Hsi Wang Mu is the high Goddess.
- Hsuan Tien Shang Ti is the God of Water.
- Hu Tu is the Goddess of Earth.
- I Ti is the God of wine.
- Kuan Ti is the God of war.
- Kuan Yin is known as The Great Mother.
- Kuei Hsing is the God of tests, exams, literature, and students.
- Lau Tien Yeh is also known as The Jade Emperor.
- Lei King is the God of Thunder.
- Lo Shen is the Goddess of rivers.
- Lu Hsing is the God of income and employment.
- Lu Pan is the God of carpenters and masons.
- Ma Ku is the Goddess of springtime.
- Men Shen are two gods who protect against evil spirits and bad influences.
- Meng Po Niang Niang is the Goddess of past-lives.
- Pa is the Goddess of droughts.
- Pi Hsia Yuan Chin is the Goddess of childbirth and labor.
- Sao Tsing Niang is the Goddess of the clouds.
Taoist Deities
- The Three Pure Ones are like a holy trinity in Taoism.
Buddhist Deities
- Laughing Buddha
- Dizang
- The Four Heavenly Kings
- Gautama Buddha
- Guanyin
Confucianism and Deities
- Confucianism does not have gods. It is a philosophy, which means it's a way of thinking about life, not a religion that worships gods.
The Eight Immortals
The Eight Immortals are not gods. They were ordinary men and women who became immortal. They earned this special gift from the gods of Taoism by living according to Taoist principles.
- Men:
- Li Tieguai
- Zhongli Quan
- Cao Guojiu
- Han Xiang
- Lu Dong-Bin
- Zhan Guojiu
- Women:
- Lan Caihe
- He Xiangu
Mythical Creatures
The Dragon
The dragon appears in most Chinese myths. It is a symbol of strength, goodness, and change. In ancient China, the original Dragon flew using magic, not wings. It had the body of a snake and the head of a horse. A special pearl was in the center of its forehead.
Some believe that Buddhists changed the dragon into an evil creature. They said dragons were filled with evil spirits.
The story of the Chinese dragon has changed over time. The first dragons were water gods. Later myths described two types of dragons: the old, friendly dragons, and the evil, winged dragons, as told by the Buddhists.
Types of Dragons
- The Green Dragon represents the power of the east.
- The Yellow Dragon represents the power of the sky.
- Blue Dragons can change their shape into blue-skinned little boys.
- The four dragon kings:
- Ao Guang is the dragon king of the eastern sea.
- Ao Chin is the dragon king of the southern sea.
- Ao Jun is the dragon king of the western sea.
- Ao Shun is the dragon king of the northern sea.
- Ao Bing, the son of Ao Guang, was a dragon with a fish head and a human body.
Mythical Birds
List of Birds
- The Red Bird represents the power of the south.
- The Phoenix is known as the emperor of all birds. The Phoenix rules over the southern part of heaven. It nests in the palace of Emperor Yao, who was known as one of the kindest emperors.
- The Crow is either the sun itself or carries the sun, depending on the myth.
- Geese are a symbol of marriage in Ancient China.
Images for kids
-
Nine Dragons, handscroll section, by Chen Rong, AD 1244, Song dynasty, Museum of Fine Arts, Boston
-
Wen Chang, Chinese God of literature, carved in ivory, c. 1550–1644, Ming dynasty.
-
Taotie ivory mask, Shang dynasty, twelfth or eleventh century BCE
-
Zhou dynasty ritual Gui (vessel) vessel (the "Kang Hou gui"), with inscription barely visible on inside bottom, British Museum
See also
 In Spanish: Mitología china para niños
In Spanish: Mitología china para niños
 | William M. Jackson |
 | Juan E. Gilbert |
 | Neil deGrasse Tyson |