Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership facts for kids
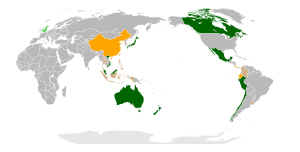
As of July 2023: Parties Signatories Formal applicants Potential applicants
|
|
| Type | Trade agreement |
|---|---|
| Signed | 8 March 2018 |
| Location | Santiago, Chile |
| Sealed | 23 January 2018 |
| Effective | 30 December 2018 |
| Condition | 60 days after ratification by 50% of the signatories, or after six signatories have ratified |
| Signatories | |
| Parties | |
| Depositary | Government of New Zealand |
| Languages | English (prevailing in the case of conflict or divergence), French, and Spanish |
The Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) is a major trade agreement. It is also known as TPP11. This agreement helps countries trade more easily with each other. It means they can buy and sell goods and services with fewer rules and taxes.
The CPTPP connects 11 countries around the Pacific Ocean. These include Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore, and Vietnam. Together, their economies are worth about $13.5 trillion. This makes the CPTPP one of the largest free-trade areas in the world. The United Kingdom formally joined the agreement in July 2023.
Contents
What is the CPTPP?
The CPTPP is a special kind of deal between countries. It aims to lower tariffs, which are taxes on imported goods. It also tries to make trade rules similar for all member countries. This makes it easier for businesses to operate across borders.
The goal is to boost economic growth for all countries involved. It also helps create more jobs. The agreement covers many areas, from farming to technology.
How the CPTPP Started
The CPTPP grew from an older agreement called the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP). The TPP was signed in 2016. However, it never officially started because the United States decided to leave it. This happened after President Donald Trump was elected.
After the U.S. left, the other 11 countries still wanted to work together. In May 2017, they agreed to revive the deal. Japan played a big role in leading this effort. In January 2018, the CPTPP was created. It kept most of the original TPP rules. Some rules that the U.S. had wanted were put on hold.
When the Agreement Began
The CPTPP was officially signed on March 8, 2018. The signing ceremony took place in Santiago, Chile. For the agreement to start, at least six of the 11 countries needed to approve it.
Australia was the sixth country to approve the agreement. This happened on October 31, 2018. Because of this, the CPTPP officially started for the first six countries on December 30, 2018. Other countries joined later as they approved the agreement.
What the Agreement Does
The CPTPP has rules about many different things. One important part is about state-owned enterprises (SOEs). These are businesses owned by a government. The agreement asks countries to share information about their SOEs. This helps make sure that governments don't unfairly control markets.
The agreement also has strong rules for intellectual property. This means protecting things like inventions, designs, and brand names. It helps companies feel safe when they operate in other countries. It protects them from their ideas being stolen.
In 2023, New Zealand was in charge of leading the CPTPP commission. This group helps manage the agreement.
See also
 In Spanish: Acuerdo Amplio y Progresista de Asociación Transpacífico para niños
In Spanish: Acuerdo Amplio y Progresista de Asociación Transpacífico para niños

