Cupuaçu facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Cupuaçu |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: |
Sterculiaceae
|
| Genus: | |
| Species: |
T. grandiflorum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Theobroma grandiflorum (Willd. ex Spreng.) K.Schum.
|
|
Cupuaçu (Theobroma grandiflorum) is a cool tree from the tropical rainforest. It's a relative of the cacao tree, which is where chocolate comes from! You might also see its name spelled as cupuassu or copoasu.
This tree grows all over the Amazon basin. It's especially popular in the jungles of Colombia, Bolivia, Peru, and northern Brazil. The biggest producers are in the Brazilian states of Pará and Amazonas.
People love the pulp from the cupuaçu fruit. It's eaten across Central and South America. You can find it in yummy treats like ice creams, snack bars, and other tasty products. The wood from the tree is also used for timber.
Contents
About the Cupuaçu Plant
Cupuaçu trees usually grow to be about 5 to 15 meters (16 to 49 feet) tall. Some can even reach up to 20 meters (65 feet)! They have brown bark.
Their leaves are quite large, about 25–35 cm (10–14 inches) long and 6–10 cm (2–4 inches) wide. Young leaves start out with a pink tint. As they get older, they turn green and eventually start to grow fruit.
Cupuaçu Flowers
The flowers of the cupuaçu tree are very special. They need help from pollinators to make fruit. Pollinators are creatures like chrysomelid weevils and stingless bees.
Heavy rains can make it hard for these tiny helpers to fly between flowers. This can affect how much fruit the trees produce.
The Amazing Cupuaçu Fruit
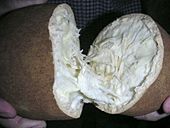
The cupuaçu fruit has white pulp inside. It has a unique smell that some people say is a mix of chocolate and pineapple. This pulp is often used in desserts, juices, and candies.
The juice tastes a bit like a pear, with a hint of banana. It's a truly tropical flavor!
Cupuaçu fruits are usually picked up from the ground after they fall naturally from the tree. It's tricky to know exactly when they are perfectly ripe. This is because the fruit doesn't change color on the outside. However, studies show that in some parts of the Amazon, fruits are fully ripe about 117 days after they start growing.
Growing Cupuaçu Trees
Most cupuaçu trees are grown from seeds. But farmers also use other methods like grafting or rooted cuttings.
These trees are often planted in special farming systems called agroforestry. This means they grow alongside other crops and trees. Cupuaçu trees are good for this because they can grow well even in poor soils. This is common in the Amazon region.
Pests and Diseases
One of the main problems for cupuaçu trees is a disease called "Witches broom." This disease can harm the whole tree. If it's not treated, it can cause a lot of fruit loss and even kill the tree. Farmers often trim the trees regularly to help control this disease.
Another creature that likes cupuaçu is a butterfly larva called "lagarta verde" (Macrosoma tipulata). These caterpillars eat the leaves of the tree.
Cupuaçu Butter
Cupuaçu butter is a special kind of fat made from the fruit's seeds. It's a mix of different fats, both saturated and unsaturated.
This butter has a low melting point, around 30 °C (86 °F). This means it melts easily and has a soft, solid texture. Because of this, it's often used in confectionery products. It can be used to make things that look and feel a bit like white chocolate.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Copoazú para niños
In Spanish: Copoazú para niños
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |