D-flat major facts for kids
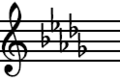 |
||
| Relative key | B♭ minor | |
|---|---|---|
| Parallel key | D♭ minor enharmonic: C♯ minor |
|
| Notes in this scale | ||
| D♭, E♭, F, G♭, A♭, B♭, C, D♭ | ||
D♭ major (or D-flat major) is a musical major scale. It is built using the note D-flat as its starting point. A major scale usually sounds bright and cheerful.
Contents
What is D-flat Major?
D-flat major is a specific set of musical notes. These notes are D-flat, E-flat, F, G-flat, A-flat, B-flat, and C. When played in order, they create the D-flat major scale.
Key Signature
Every musical key has a key signature. This is a group of sharps or flats shown at the start of a piece of music. The key signature for D-flat major has five flats. These flats are on the notes B, E, A, D, and G. This means that these notes are always played as flats unless changed by a special symbol.
Related Keys
Musical keys often have "relatives." These are other keys that share many notes.
Relative Minor Key
The relative minor key of D-flat major is B♭ minor. Relative keys share the same key signature. This means B-flat minor also has five flats. Minor keys often sound more serious or sad than major keys.
Parallel Minor Key
The parallel minor key of D-flat major is D♭ minor. Parallel keys start on the same note. However, D-flat minor is rarely used in music. This is because its key signature would need eight flats, including a double-flat. This makes it very difficult to read and play.
C-sharp Minor: A Common Replacement
Instead of D-flat minor, composers often use C♯ minor. C-sharp minor sounds exactly the same as D-flat minor. It is called an enharmonic key. C-sharp minor is much easier to read because it only has four sharps.
Famous Music in D-flat Major
Many famous composers have written music in D-flat major. This key is often chosen for its rich and warm sound.
Chopin's "Raindrop" Prelude
Frédéric Chopin used D-flat major in his famous Prelude No. 15, known as the "Raindrop" Prelude. In the middle part of this piece, the music changes to C-sharp minor. This change creates a different mood, moving from the bright D-flat major to the more thoughtful C-sharp minor.
Other Examples
- In Chopin's Fantaisie-Impromptu, the main part is in C-sharp minor. But the beautiful middle section switches to D-flat major. This creates a lovely contrast.
- Claude Debussy's well-known piece Clair de lune also changes from D-flat major to C-sharp minor in a key section.
- Antonín Dvořák's New World Symphony also uses C-sharp minor for a short time in its slow movement.
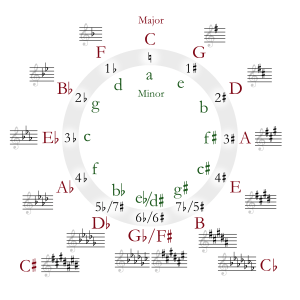
| Diatonic Scales and Keys | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The table shows the number of sharps or flats in each scale. Minor scales are written in lower case. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
 In Spanish: Re bemol mayor para niños
In Spanish: Re bemol mayor para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |