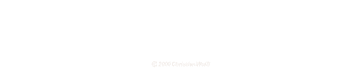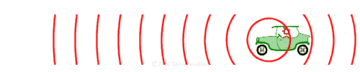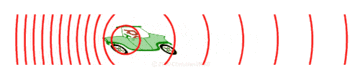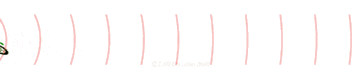Doppler effect facts for kids
The Doppler effect is a cool science idea that explains why the sound of a siren changes as an emergency vehicle drives past you. Imagine a police car or ambulance with its siren on. When it's coming towards you, the sound seems higher pitched. But as it passes and moves away, the sound gets lower pitched. This change in sound is called the Doppler effect, and it happens because of how waves, like sound waves, behave when their source or the listener is moving. It's named after a scientist named Christian Doppler, who first explained it in 1842.
Contents
What is the Doppler Effect?
How Does it Work?
The Doppler effect happens because waves, like sound waves, travel through a medium (like air or water). When something that makes a sound (the source) moves, it changes how those waves spread out.
Imagine a sound source, like a speaker, standing still. It sends out sound waves in perfect circles, like ripples in a pond. The distance between these ripples is the wavelength, and how many ripples pass you each second is the frequency (which we hear as pitch).
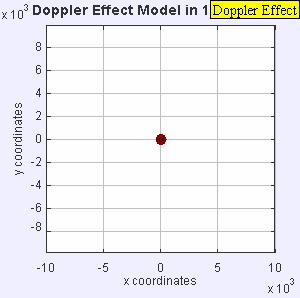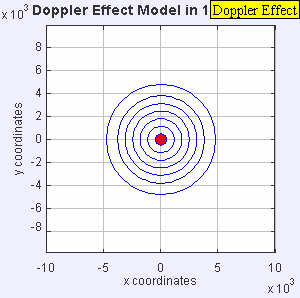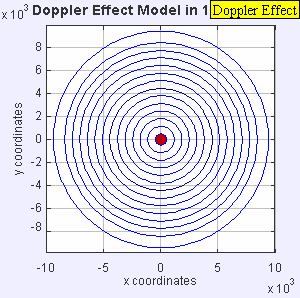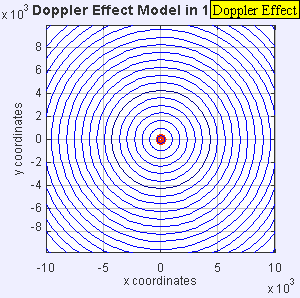
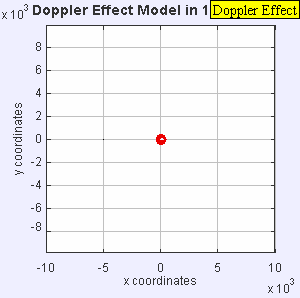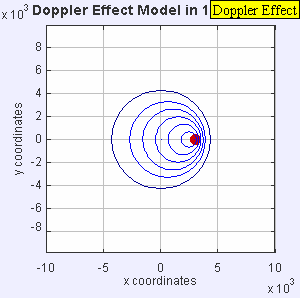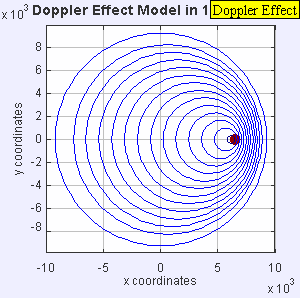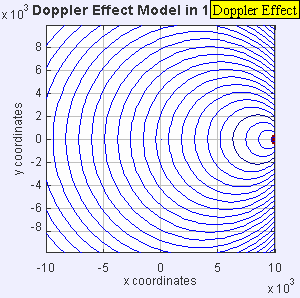
Now, imagine the speaker starts moving towards you. As it moves, it sends out new waves from a slightly closer spot each time. This makes the waves in front of the speaker get squished together. When waves are squished, their wavelength gets shorter, and more waves reach you every second. This means the frequency goes up, and you hear a higher pitch!
If the speaker moves away from you, the opposite happens. Each new wave is sent out from a spot farther away. This stretches out the waves behind the speaker. When waves are stretched, their wavelength gets longer, and fewer waves reach you each second. This means the frequency goes down, and you hear a lower pitch.
This effect isn't just for sound. It also works for other types of waves, like light waves or radio waves. For light waves, which can travel through empty space (a vacuum), the effect depends only on how fast the source and the observer are moving relative to each other.
-
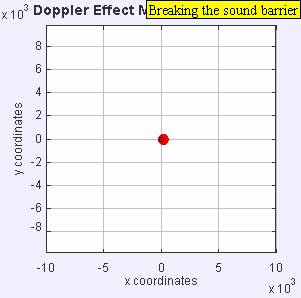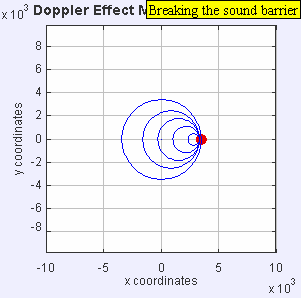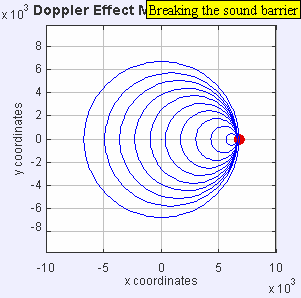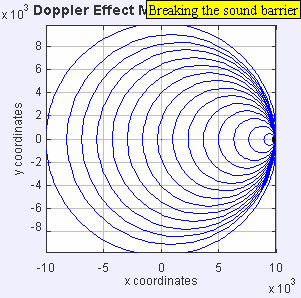
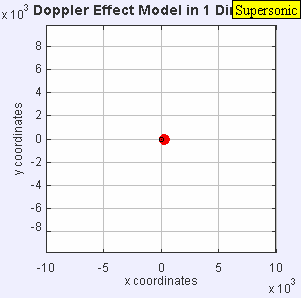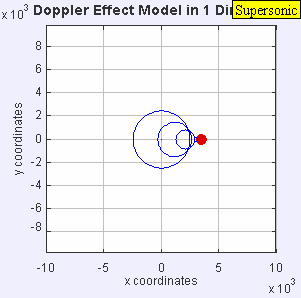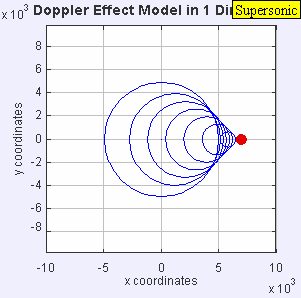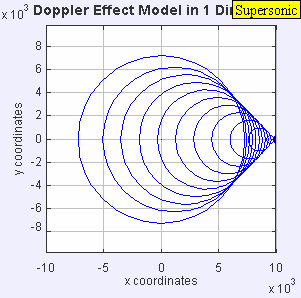
If the source moves faster than sound, it leaves the sound waves behind, creating a sonic boom.
A Look Back in Time: History
The idea of the Doppler effect was first suggested by Christian Doppler in 1842. He wrote about it in a paper about the light from binary stars (two stars orbiting each other).
A few years later, in 1845, a scientist named C. H. D. Buys Ballot decided to test Doppler's idea using sound waves. He did an experiment where musicians played trumpets on a moving train! He found that the sound's pitch really did change, just as Doppler predicted. It was higher when the train came closer and lower when it moved away.
Another scientist, Hippolyte Fizeau, also discovered this effect for light waves in 1848, but Doppler had already published his work first.
What Happens at High Speeds?
If a sound source moves faster than the speed of sound, it creates a powerful shock wave. This is what causes a sonic boom, which is a loud noise like an explosion! You might hear this when a jet airplane flies overhead very fast.
A scientist named Lord Rayleigh once imagined something amazing: if you could move away from a sound source at twice the speed of sound, you would hear music played by that source, but it would sound like it was playing backwards!
Where Do We See It? Real-Life Examples
Sirens and Emergency Vehicles
The most common example of the Doppler effect is hearing a siren on an emergency vehicle like an ambulance or fire truck. When the vehicle is coming towards you, the siren sounds higher pitched. As it passes you, the pitch quickly drops. Then, as it drives away, the siren sounds lower pitched. This happens because the vehicle isn't driving straight at you and then suddenly away; it's moving past you, so the angle of its movement changes how the sound waves reach your ears.
Exploring Space: Astronomy
The Doppler effect is super important in astronomy! Scientists use it to figure out if stars and galaxies are moving towards us or away from us.
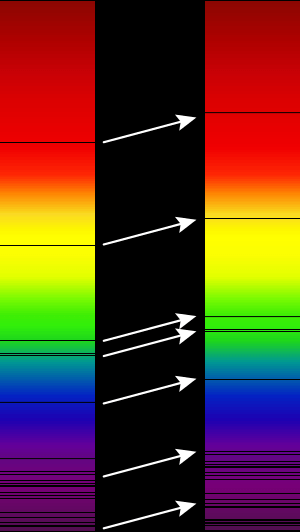
When a star or galaxy moves away, its light waves get stretched out, making them appear redder. This is called redshift. If it's moving towards us, the light waves get squished, making them appear bluer. This is called blueshift.
By looking at these tiny shifts in light, astronomers can:
- Find out how fast stars and galaxies are moving.
- Discover if a single star is actually two stars orbiting each other (a binary star).
- Measure how fast galaxies are spinning.
- Even find exoplanets (planets outside our solar system) by seeing how they make their star "wobble."
You can't see these color changes with your eyes, but special tools can detect them.
Catching Speeders: Radar
Have you ever seen a police officer using a radar gun? These devices use the Doppler effect!
A radar gun sends out radio waves. When these waves hit a moving car, they bounce back. If the car is moving towards the radar gun, the waves that bounce back get squished (higher frequency). If the car is moving away, the waves get stretched (lower frequency). By measuring how much the waves change, the radar gun can figure out exactly how fast the car is moving. This is a very accurate way to measure speed!
Inside Our Bodies: Medical Uses
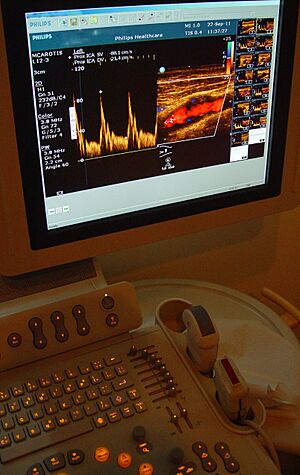
Doctors use the Doppler effect to see what's happening inside our bodies, especially with blood flow!
A special type of ultrasound called "Doppler ultrasound" sends sound waves into your body. When these waves hit moving blood, they bounce back with a changed frequency. By measuring this change, doctors can:
- See how fast blood is flowing.
- Check the direction of blood flow.
- Look at how well your heart valves are working.
- Find problems in blood vessels, like blockages.
This helps them diagnose many health conditions without needing to do surgery.
Measuring Flow in Liquids
The Doppler effect is also used in tools that measure how fast liquids are flowing. For example, a laser Doppler velocimeter uses a laser beam. When the laser light hits tiny particles moving in a liquid, the light that bounces back changes frequency. By measuring this change, scientists can figure out the speed of the liquid flow very precisely. This is useful in many areas, from studying rivers to designing pipes.
Seeing How Liquids Move
Similar to how it's used in medicine, a technique called Ultrasonic Doppler Velocimetry (UDV) can measure the full "speed map" of liquids. It can see how fast different parts of a liquid are moving, even if the liquid has tiny particles, bubbles, or is moving in complex ways. This helps scientists understand how liquids behave.
Satellites in Space
The Doppler effect is very important for satellite navigation and satellite communication.
Satellites move very fast, so the radio signals they send to Earth (or receive from Earth) experience a big Doppler shift. Engineers have to carefully adjust the frequencies of these signals so that the satellite and the ground station can communicate clearly.
For example, when the Huygens probe was sent to Titan (a moon of Saturn), scientists realized they needed to adjust its path. If they didn't, the Doppler effect would have made its radio signals too hard for the main Cassini–Huygens spacecraft to receive! They changed the probe's path so its signals would have less Doppler shift, making sure the important data got through.
Cool Sounds: Audio
Some musical instruments and speakers use the Doppler effect to create unique sounds. A great example is the Leslie speaker, often used with a Hammond organ. This speaker has a rotating horn inside. As the horn spins, the sound it sends out changes pitch slightly due to the Doppler effect, creating a cool, swirling, vibrating sound that musicians love.
Measuring Vibrations
Scientists and engineers use a tool called a laser Doppler vibrometer to measure how much things are vibrating. It works by shining a laser beam onto a surface. If the surface is vibrating, the laser light that bounces back will have a tiny Doppler shift. By measuring this shift, the tool can figure out exactly how much and how fast the surface is vibrating without even touching it.
Robots on the Move
The Doppler effect can even help robots! In complex environments where things are constantly moving (like in robot competitions or "robosoccer"), robots can use the Doppler effect to detect how fast obstacles are moving. This helps them plan their own movements safely and efficiently, avoiding crashes.
The "Backwards" Doppler Effect
Scientists have also thought about something called the inverse Doppler effect. This is a very special and unusual version of the effect. It happens in certain rare materials that can bend waves in a very strange way. In these materials, the Doppler shift would work in the opposite direction of what we normally expect. So, if a source was moving towards you, the frequency might actually go down instead of up! Scientists first saw this "backwards" effect in experiments in 2003.
See also
 In Spanish: Efecto Doppler para niños
In Spanish: Efecto Doppler para niños
- Bistatic Doppler shift
- Differential Doppler effect
- Doppler cooling
- Dopplergraph
- Fading
- Fizeau experiment
- Photoacoustic Doppler effect
- Range rate
- Rayleigh fading
- Redshift
- Laser Doppler imaging
- Relativistic Doppler effect