El Niño–Southern Oscillation facts for kids
The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (called ENSO for short) is a natural event that happens in the Pacific Ocean. It is also known as El Niño and La Niña. These names are Spanish words. "El Niño" means "little boy," and "La Niña" means "little girl."
ENSO is a big climate pattern that affects weather around the world. It involves changes in ocean temperatures and air pressure. These changes can lead to very different weather conditions.
Contents
What is El Niño?
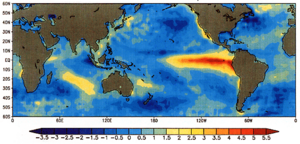
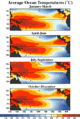
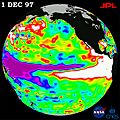
El Niño happens when the surface water in the tropical Pacific Ocean gets warmer than usual. This event usually occurs every two to seven years.
- A weak, warm ocean current often starts around Christmas. It flows along the coasts of Ecuador and Peru.
- Sometimes, this warming lasts only a few weeks.
- Other times, a strong El Niño can last for many months.
- When El Niño is strong, it can change weather patterns globally. For example, Australia and Southeast Asia might have droughts. But the deserts of Peru could get very heavy rainfall. East Africa might experience both.
What is La Niña?
La Niña is the opposite of El Niño. During a La Niña event, the surface water in the tropical Pacific Ocean becomes colder than usual.
- The weather patterns during La Niña are often reversed from El Niño.
- For example, areas that had droughts during El Niño might get more rain during La Niña.
- La Niña can also cause major weather events. The 2010–2011 Queensland floods in Australia were caused by a strong La Niña. This event brought very heavy rain to Australia's east coast. Other big floods in Australia also happened during La Niña years.
The Southern Oscillation
The Southern Oscillation is linked to El Niño and La Niña. It was discovered in 1923 by Sir Gilbert Walker.
- It's like a "seesaw" of atmospheric pressure between the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
- Scientists measure air pressure at two places: Darwin, Australia (in the Indian Ocean) and Tahiti (in the South Pacific).
- When the pressure is high in one place, it's usually low in the other.
- This pressure difference helps scientists know if an El Niño or La Niña is happening. By the early 1980s, it became clear that El Niño and the Southern Oscillation were connected. That's why the term ENSO is used for this large climate event.
Different Kinds of El Niño
Not all El Niño events are exactly the same. Scientists have found that some El Niños happen in the Central Pacific Ocean. These are called Central Pacific El Niños.
- The effects of Central Pacific El Niños can be different from the more traditional El Niños that start closer to South America.
- Some Central Pacific El Niños have happened in recent years, such as in 1986–88, 1991–92, 1994–95, 2002–03, 2004–05, 2006–07, 2009–10, and 2015–16.
Images for kids
-
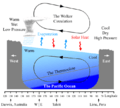
Diagram of the quasi-equilibrium and La Niña phase of the Southern Oscillation. The Walker circulation is seen at the surface as easterly trade winds which move water and air warmed by the sun towards the west. The western side of the equatorial Pacific is characterized by warm, wet low pressure weather as the collected moisture is dumped in the form of typhoons and thunderstorms. The ocean is some 60 centimetres (24 in) higher in the western Pacific as the result of this motion. The water and air are returned to the east. Both are now much cooler, and the air is much drier. An El Niño episode is characterised by a breakdown of this water and air cycle, resulting in relatively warm water and moist air in the eastern Pacific.
See also
 In Spanish: El Niño-Oscilación del Sur para niños
In Spanish: El Niño-Oscilación del Sur para niños