European scops owl facts for kids
The Eurasian scops owl is a small and interesting bird. It's also called the European scops owl or simply scops owl. This little owl belongs to the typical owl family, called Strigidae. These owls live and raise their young in places from southern Europe all the way to southern Siberia and the western Himalayas. When winter comes, they fly south to Africa, below the Sahara Desert, because they are migratory birds.
Quick facts for kids European scops owl |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Eurasian scops owl
|
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Strigiformes |
| Family: | Strigidae |
| Genus: | Otus |
| Species: |
O. scops
|
| Binomial name | |
| Otus scops (Linnaeus, 1758)
|
|
 |
|
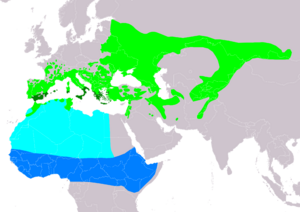
| Range of O. scops Breeding Resident Passage Non-breeding | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Strix scops Linnaeus, 1758 |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Contents
How Scientists Name Them
Scientists use a special system to name and group all living things. This is called Taxonomy. The Eurasian scops owl was first officially described by a Swedish scientist named Carl Linnaeus in 1758. He put it in a group with other owls called Strix.
Later, in 1769, another scientist named Thomas Pennant created a new group just for owls like the scops owl. This new group was called Otus. The name Otus comes from a Latin word that means "eared owl." The word scops comes from an ancient Greek word for a small eared owl.
There are five different types, or subspecies, of the Eurasian scops owl:
- O. s. scops: Found from France and Italy to the Caucasus area.
- O. s. mallorcae: Lives in the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal), the Balearic Islands, and northwest Africa.
- O. s. cycladum: Found in southern Greece, Crete, southern Turkey, Syria, and Jordan.
- O. s. turanicus: Lives from Iraq to northwest Pakistan.
- O. s. pulchellus: Found from Kazakhstan to southern Siberia and the western Himalayas.
What They Look Like
The Eurasian scops owl is quite small. It is about 19 to 21 centimeters (about 7.5 to 8.3 inches) long. Its wings can spread out to about 47 to 54 centimeters (about 18.5 to 21 inches). This makes it a bit smaller than the little owl.
When it perches, it sits very straight. It has small ear-tufts, which are feathers that look like ears. Its feathers, called its plumage, are mostly grey-brown. Its face, belly, and a line on its shoulder are lighter in color. This owl flies in a strong, straight way using its long, narrow wings. This is helpful for its long migratory journeys.
The call of this owl is a deep whistle. Both male and female owls make this sound. It can sound a bit like the call of midwife toads.
Where They Live
These owls breed, or have their young, in southern Europe and across western and central Asia. They are migratory birds. This means they fly south for the winter to the southernmost parts of Europe and to Africa, south of the Sahara Desert.
Sometimes, they are seen further north than their usual breeding areas. This usually happens in spring when they might fly a bit too far. It's rare to spot this owl outside of its breeding season because it is a nocturnal bird and doesn't call as much then.
How They Behave
Raising Their Young
Eurasian scops owls like to breed in open woodlands, parks, and gardens. They usually make their nests in holes in trees or walls. Sometimes, they might use an old nest built by another bird, like a crow.
A female owl usually lays 4 or 5 eggs. These eggs are white and measure about 31 by 27 millimeters (about 1.2 by 1.1 inches). Each egg weighs around 13 grams (about 0.46 ounces). Only the female owl sits on the eggs to keep them warm. The eggs hatch after about 24 to 25 days. Both parents take care of and feed the young owls. The young owls learn to fly when they are about 21 to 29 days old. They become independent from their parents when they are 30 to 40 days old.
What They Eat
The Eurasian scops owl eats small prey. This mostly includes insects and other small creatures without backbones, called invertebrates. They hunt mostly at night because they are nocturnal.
Images for kids




