Fort Bedford facts for kids
Fort Bedford was an important British fort built during the French and Indian War. It was located where the town of Bedford, Pennsylvania is today. The fort was shaped like a star and made of logs. It was built in the summer of 1758.
Contents
Why Fort Bedford Was Built
Fort Bedford was built during the French and Indian War by British soldiers. Colonel Henry Bouquet led the building project, following orders from General John Forbes.
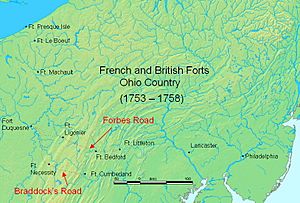
This fort was one of many forts and small blockhouses the British built. Their main goal was to protect their supply lines along the Forbes Road. This road was a new path cut through the wild lands of Pennsylvania. The British used it to move their army and supplies when they marched to attack the French fort, Fort Duquesne, which is now Pittsburgh.
Before this, General Edward Braddock had tried to capture Fort Duquesne but failed badly. General Forbes learned from Braddock's mistakes. Braddock had started his attack from western Maryland with few supplies. His supply lines were easily cut off.
General Forbes planned a bigger attack from eastern Pennsylvania. He decided to build a new wagon road over the Allegheny Mountains. His plan included building many forts and blockhouses along the way. These forts would protect the supply road from attacks by Native American groups.
After building Fort Juniata Crossing near what is now Breezewood, Pennsylvania, Colonel Bouquet started planning Fort Bedford. It was the next step on the way to the Ohio Country.
Where and How Fort Bedford Was Built
Colonel Bouquet chose a spot next to the Juniata River. It was west of a special gap in Evitt Mountain called "the Narrows." The new fort was about a day's walk from the previous fort, which fit the overall plan.
A trading post owned by John Wray was located just west of the Narrows. The new fort was built on a high area above a part of the Juniata River. It was about a mile west of Wray's trading post, which was known as 'Raystown.' Because it was the most important place in the area, the new fort was often called the "camp at Raystown" or the "camp near Raystown." Later, the fortified supply base was named Fort Bedford to honor John Russell, the 4th Duke of Bedford.
Bouquet spent time looking for a good spot. He needed a place that was easy to defend and had fresh water. Since he couldn't find one spot with both, the builders put the fort on a high spot. They then built a special protected walkway that went down to the Juniata River for water. It is thought that Fort Bedford was the only fort in America built with this unique way to get water.
The exact spot of the original fort is not fully known today. However, archaeological digs have found signs of the fort's walls. These findings suggest the fort was just north of today's Pitt Street and west of Richard Street. Old maps from 1758 and 1766 have also helped to guess where the fort might have been.
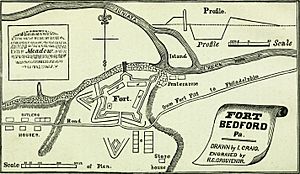
The fort was a star-shaped fortress made of logs. It had five points, called bastions. The walls covered an area of about 1.45 acres (about 5,868 square meters). The main entrance was on the south side and was protected by an earthen mound called a ravelin. The north side, which faced the river, had the special walkway to the riverbank. The other sides of the fort were protected by a ditch that was about 4 to 9 feet (1.2 to 2.7 meters) deep.
The fort's powder magazine, where gunpowder was stored, is believed to have been at the site of 111 S. Juliana Street today. The building there has an original two-story part built in 1758, at the same time as the fort. It is thought to be the only original building from the French and Indian War still standing in the United States. Later, a log addition was built onto the east wall of this building between 1789 and 1811. Another wooden structure was added to the east wall of the log part around the 1830s.
Fort Bedford's Role in History
Fort Bedford was very important during the French and Indian War. It was like a "Grand Central Station" for the British army's push westward. It served as a main gathering point and storage area for supplies. Colonel Bouquet and General Forbes even used it as their headquarters for parts of the campaign.
After most of the army moved west, about 800 soldiers stayed at the fort. The fort did not see much direct fighting during the war. It was mainly used as a supply base closer to the front lines.
As the French and Indian War ended in the frontier, the soldiers from Fort Bedford were moved to other forts. When Pontiac's War began, Captain Lewis Ourry was in charge of Fort Bedford. He had only twelve soldiers to guard the fort and more than 90 local families. Even though the fort was not strongly guarded, it was not directly attacked by Native American warriors. Instead, they raided nearby settlements and attacked supply wagons heading for the fort. They hoped to make the soldiers inside the fort run out of food. When more soldiers arrived with Colonel Bouquet in July 1763, most of the local raids stopped.
Details about the fort between the wars are not very clear. The British Army left the fort sometime during this period. According to the story of James Smith, a leader of a colonial group called the "Black Boys", he and his men captured the fort in 1769. This story is only found in Smith's own book. Some historians believe it might be true, while others are not sure. Smith called this the first British fort to fall in the time leading up to the American Revolution. This event was shown in the 1939 movie Allegheny Uprising, starring John Wayne as James Smith.
However, other evidence suggests Smith's story might not be completely accurate. In 1766, a man named Garrett Pendergrass asked the governor for money because his property was used by the army. He said that "since the King's Troops evacuated that Fort..." This means the British soldiers had already left the fort by 1766. So, if James Smith attacked Fort Bedford in 1769, three years after the British left, he would have attacked an empty fort. Also, court records from that time do not mention Smith capturing a 'British Fort.' No one knew about the fort being captured until Smith published his book thirty years later.
During the Revolutionary War, the fort was used by local soldiers who supported the American side. These soldiers guarded the frontier settlers from attacks by Seneca warriors who were allied with the British. British officers would lead small groups of soldiers and many Seneca warriors to attack isolated farms. They would capture families and then ambush the local soldiers who came to rescue them. Their main goal was to capture American officers to trade for their own captured officers.
What Happened to Fort Bedford
After the American War of Independence ended, new peace agreements were made in the 1780s. These agreements, like the Treaty of Fort Stanwix and the Treaty of Fort McIntosh, made people less afraid of Native American raids in the area. Sometime during this period, the fort was left empty and taken apart.
When George Washington led troops to western Pennsylvania in 1794 to stop the Whiskey Rebellion, he stopped in Bedford. Records from that time suggest the fort was already falling apart. Local people had started taking logs from the fort's walls and buildings to use for their own homes. It is believed that the log addition built onto the powder magazine building used logs that originally came from the fort.
In 1958, a new building was constructed near the original site to look like one of the fort's five log blockhouses. This was done to celebrate the fort's 200th anniversary. The style of this new building might not be exactly like the original blockhouses of Fort Bedford, because there are no pictures of the original fort from that time. Unlike most blockhouses from the French and Indian War, this new building looks more like blockhouses from the 1870s in the American Midwest. Today, this reconstructed blockhouse is a museum run by The Bedford Heritage Trust.
|