French period facts for kids
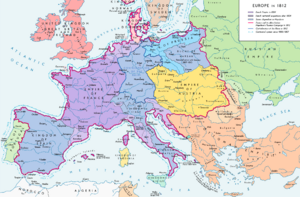
The French period is a name used in Northern Europe to describe the time between 1794 and 1815. During these years, most of Northern Europe was under the control of France, first as a republic and later as an empire led by Napoleon. The exact length of this period changed depending on the country.
In Germany, this term became popular in the 1800s. It was sometimes used to express strong anti-French feelings as Germans started to form their own national identity. Because of this, the term "French period" is not often used in Germany today. Instead, people usually say "French Revolutionary Wars" and "Napoleonic Wars" to describe this time.
In the Netherlands, the time when Napoleon made his younger brother Louis king of the Kingdom of Holland is part of this period. This happened after the Batavian Republic was overthrown.
How France Gained Control
After a big battle called the Battle of Austerlitz and a war known as the War of the Third Coalition, Napoleon made major changes in Europe. He ended the Holy Roman Empire, which had existed for a very long time. He also added parts of Austria and some German states directly to France.
Napoleon then created a group of German states called the Confederation of the Rhine. He was their "protector," which meant he had a lot of power over them. These states had to follow France's foreign policy and provide many soldiers for Napoleon's army.
People were not happy about being forced to join the army. This led to an uprising in 1798, known as the Peasants' War, in areas that are now Belgium and Luxembourg.
In Germany, Napoleon created two new states: the Grand Duchy of Berg and the Kingdom of Westphalia. He gave these to his general, Joachim Murat, and his brother, Jerome Bonaparte. The Austrian Netherlands and the Prince-Bishopric of Liège were also taken over by France and became French départements (like provinces).
During this time, France introduced new laws called the Napoleonic Code. This code brought new ideas from the French Revolution, like the idea of nationalism, which is a strong feeling of pride and loyalty to one's own country.
In Prussia, which was a powerful German state, the French occupation led to big changes. Even though Prussia wasn't part of Napoleon's Confederation, it was still occupied by French forces. This situation pushed Prussia to make important reforms in its government, society, and military. These changes were very important later during the "Liberation War" against France.
As the French army suffered a terrible defeat during the French invasion of Russia, the Prussian commander, Yorck, signed a ceasefire with Russia. This event was a major turning point and helped start the Liberation War.
What Happened After?
The French period played a big part in creating a sense of unity and national identity in Germany. People from different regions, speaking various dialects, found a common purpose in fighting against French control. This struggle helped them see themselves as "Germans" who shared a desire for freedom.
After this period, there was a time when the desire for freedom from government control was suppressed. However, these feelings eventually led to the March Revolution in 1848. This revolution led to the formation of the first German parliament, though not all German-speaking areas were included.
During the Prussian War of Liberation, a new system for drafting soldiers was introduced. This system was similar to the French levée en masse (mass conscription) and was part of the Prussian army reforms. The Prussian reforms, which happened between 1807 and 1812, were some of the biggest political and social changes in Germany between the Early Modern Period and the Modern Period.
When Francis II gave up the title of Holy Roman Emperor and became the Emperor of Austria, it created a political separation between Prussia and Austria. This separation later led to Austria being excluded from the "German Question", which was about how to unify Germany.
Images for kids