Gaia hypothesis facts for kids
The Gaia hypothesis, also known as Gaia theory, suggests that all living things on Earth work together with their non-living surroundings, like the air, water, and rocks. They form a huge, complex system that helps keep our planet just right for life to continue. Think of Earth as a giant, self-regulating system!
This interesting idea was first developed in the 1970s by a scientist named James Lovelock and later supported by biologist Lynn Margulis. They named it after Gaia, the ancient Greek goddess of Earth.
Contents
What is the Gaia Hypothesis?
The Gaia hypothesis proposes that Earth's living organisms and their non-living environment are deeply connected. They constantly interact to keep conditions stable for life. This means things like the temperature, the amount of salt in the oceans, and the gases in the air are all influenced and managed by life itself.
Earth as a Self-Regulating System
Imagine your body. It keeps your temperature steady, even when it's cold or hot outside. It also controls your breathing and heart rate. The Gaia hypothesis suggests that Earth does something similar on a much larger scale.
For example, plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. This helps control the amount of these gases in the atmosphere, which is important for keeping the planet from getting too hot or too cold. Microbes in the ocean also play a big role in regulating the climate.
How Life Affects the Planet
Life on Earth has changed the planet dramatically over billions of years.
- Atmosphere: Early Earth had very little oxygen. But tiny organisms like cyanobacteria started producing oxygen through photosynthesis. Over time, this built up the oxygen-rich atmosphere we breathe today.
- Temperature: The Earth's temperature has stayed within a range suitable for life for a very long time, even though the sun has gotten hotter. The Gaia hypothesis suggests that life helps regulate this temperature.
- Oceans: Marine life helps control the saltiness and chemistry of the oceans.
Who Developed the Idea?
The Gaia hypothesis was mainly developed by two important scientists:
James Lovelock
James Lovelock was a British independent scientist, inventor, and environmentalist. He first thought of the Gaia idea while working for NASA in the 1960s. He was trying to figure out if there was life on Mars. He realized that if Mars had life, its atmosphere would probably be very different from what it is. Earth's atmosphere, on the other hand, seemed to be actively managed by life.
Lynn Margulis
Lynn Margulis was an American evolutionary biologist. She joined Lovelock in developing the Gaia hypothesis. Her work on how different organisms came together to form complex cells (called endosymbiosis) helped strengthen the idea that life is deeply interconnected and influences its environment.
Understanding Daisyworld
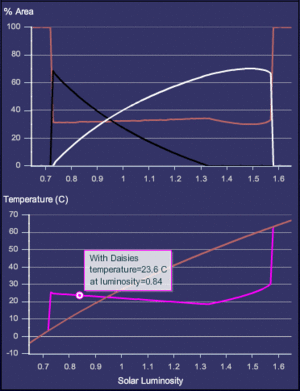
To help explain the Gaia hypothesis, James Lovelock created a simple computer model called "Daisyworld."
What is Daisyworld?
Daisyworld is a made-up planet where the only living things are black and white daisies.
- Black daisies absorb more sunlight, making the ground around them warmer.
- White daisies reflect more sunlight, making the ground around them cooler.
As the sun's heat changes, the daisies compete and grow. If the planet gets too hot, white daisies thrive and cool it down. If it gets too cold, black daisies thrive and warm it up. This simple model shows how life can regulate the planet's temperature, even without any conscious effort from the daisies. It's a great way to see how self-regulation might work on Earth.
Why is Gaia Important?
The Gaia hypothesis helps us understand our planet in a new way. It shows us that Earth is not just a collection of separate parts, but a single, interconnected system.
Impact on Environmental Science
This idea has influenced how scientists think about climate change and environmental issues. If Earth is a self-regulating system, then human activities that disrupt this system could have big consequences. It highlights the importance of keeping our planet healthy, as all parts are connected.
Is Earth Alive?
The Gaia hypothesis doesn't mean Earth is a living organism in the same way an animal or plant is. It's more about Earth acting like a superorganism or a complex system that maintains conditions for its own survival and the survival of life on it. It's a way of looking at the planet as a whole, rather than just separate parts.
Images for kids
-
The study of planetary habitability is partly based upon extrapolation from knowledge of the Earth's conditions, as the Earth is the only planet currently known to harbour life (The Blue Marble, 1972 Apollo 17 photograph)
-
Levels of gases in the atmosphere in 420,000 years of ice core data from Vostok, Antarctica research station. Current period is at the left.
-
Earthrise taken from Apollo 8 by astronaut William Anders, December 24, 1968
See also
 In Spanish: Hipótesis Gaia para niños
In Spanish: Hipótesis Gaia para niños