Hanafi facts for kids
The Hanafi school is the oldest of the four main schools of law within Sunni Islam. These schools are like different ways of understanding and applying Islamic law, called Fiqh (jurisprudence). Each school, also known as a Madhhab, offers a specific method for interpreting religious texts and solving new legal questions.
Contents
What is the Hanafi School?
The Hanafi school is one of the most followed Madhhabs in the world. It is known for its focus on using reason and logic, alongside the traditional sources of Islamic law. This approach helps scholars find solutions to new problems that weren't directly mentioned in early Islamic texts.
Who Founded the Hanafi School?
The Hanafi school was founded by a famous scholar named Imam Abu Hanifa. He lived in the 8th century (around 699–767 CE) in a city called Kufa, which is in modern-day Iraq. Imam Abu Hanifa was known for his deep knowledge and his unique way of thinking about legal issues. His students wrote down his teachings, and these teachings became the foundation of the Hanafi school.
How Did it Develop?
After Imam Abu Hanifa, his students and later scholars continued to develop his ideas. They created a detailed system of law that covered many aspects of daily life, from prayers and charity to business and family matters. This system became very popular and was adopted by many rulers and empires throughout history.
Where is the Hanafi School Followed?
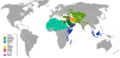
The Hanafi school is widely followed in many parts of the world. It is the main school of law in countries like Turkey, much of Central Asia, and large parts of South Asia, including Pakistan and Bangladesh. You can also find many Hanafi followers in the Southeast Europe, China, Russia, and parts of the Middle East. About one-third of all Muslims in Muslim-majority countries follow Hanafi law.
Why is it So Widespread?
One reason for the Hanafi school's wide reach is that it was the official legal system of several powerful empires, including the Abbasid Caliphate and the Ottoman Empire. As these empires expanded, they brought the Hanafi legal system with them, and it became deeply rooted in the cultures of those regions. Its practical and logical approach also made it appealing to many different communities.
Key Ideas of the Hanafi School
The Hanafi school uses several important sources to make legal decisions:
- The Quran: This is the holy book of Islam.
- The Sunnah: These are the sayings and actions of the Prophet Muhammad.
- Ijma (Consensus): This refers to the agreement of Islamic scholars on a particular issue.
- Qiyas (Analogical Reasoning): This is a method of comparing new situations to similar ones that have already been decided, using logic to find a solution. The Hanafi school is especially known for its emphasis on this method.
- Istihsan (Juristic Preference): This means choosing a solution that is more fair or practical, even if it slightly deviates from a strict interpretation of a rule.
These methods help Hanafi scholars adapt Islamic law to changing times and new challenges, while still staying true to its core principles.
Images for kids
-
Map of the Muslim world. Hanafi (light green) is the Sunni school predominant in Turkey, the Western Middle East, Western and Nile river region of Egypt, Central Asia, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and parts of Southeast Europe, India, China and Russia. An estimated third of all Muslims living in Muslim-majority countries worldwide follow Hanafi law.
See also
 In Spanish: Hanafí para niños
In Spanish: Hanafí para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |