Hapi facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Hapi |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Upper part of a statue of the Nile God Hapi. From Faiyum, Egypt, 12th Dynasty, c. 1800 BCE. Neues Museum, Berlin
|
|||||
| Name in hieroglyphs |
|
||||
| Major cult center | Elephantine | ||||
| Symbol | Lotus plant | ||||
Hapi was an important god in ancient Egyptian religion. He was the god of the yearly flooding of the Nile River. This flood was super important because it brought rich, fertile soil to the riverbanks. This soil helped the Egyptians grow all their crops.
Because of how helpful he was, Hapi was greatly celebrated. People called him "Lord of the Fish and Birds of the Marshes." They also called him "Lord of the River Bringing Vegetation." Hapi is often shown as a figure with both male and female features. He has a big belly, wears a loincloth, and sometimes a fake beard.
Hapi's Story and Role
The yearly flooding of the Nile was sometimes called the Arrival of Hapi. This flood made the land fertile, meaning it was good for growing food. This was very important in a desert land like Egypt. So, Hapi became a symbol of good harvests and new life.
Because he brought so much life, some people even called Hapi the "father of the gods." He was seen as a caring father who helped keep the world balanced and orderly.
People believed Hapi lived inside a secret cave. This cave was thought to be near Aswan, where the Nile River was believed to start.
Worship of Hapi
The main place where Hapi was worshipped was at a spot called the First Cataract. This area was near Elephantine. Priests of Hapi performed special rituals there. They wanted to make sure the annual flood was just right. It needed to be high enough to bring fertile soil but not too high to cause damage.
It's important to know that Hapi was not the god of the Nile River itself. Instead, he was the god of the flood event. He was also considered a good friend of Geb, who was the Egyptian god of the earth. Hapi was also known as the "lord of Neper," the god of grain.
Gallery
-
Hapi is featured on the back of the E£5 note.
-
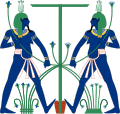
This image shows Hapi as two figures. They are symbolically tying together Upper and lower Egypt.
 | George Robert Carruthers |
 | Patricia Bath |
 | Jan Ernst Matzeliger |
 | Alexander Miles |