Heat transfer facts for kids
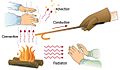
Heat transfer is how warmth moves from one place or object to another. It happens when there's a difference in temperature. Heat always travels from warmer things to cooler things. This can happen with solids, liquids, or gases. There are three main ways heat moves: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Contents
How Materials Change State
A phase change (or phase transition) is when a material changes from one state to another because of heat. Think of ice melting into water, or water boiling into steam.
There are four main states of matter:
- Solid – Changes like freezing (liquid to solid) or deposition (gas to solid).
- Gas – Changes like boiling (liquid to gas) or sublimation (solid to gas).
- Liquid – Changes like melting (solid to liquid) or condensation (gas to liquid).
- Plasma – Changes like ionization (gas to plasma).
Boiling Water
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature where its liquid turns into a gas very quickly. This happens when the vapor pressure of the liquid matches the pressure around it.
When a liquid reaches its "saturation temperature," it means it has absorbed enough heat to start boiling. If you add any more heat, it will change into a gas.
When water is at a normal pressure and not too hot, it doesn't boil. Heat moves in the usual way. As the surface gets hotter, tiny bubbles of vapor start to form, grow, and then disappear. This is called sub-cooled nucleate boiling, and it's a very good way to transfer heat. If too many bubbles form, they can get in the way, and the heat transfer might not increase as fast.
At higher temperatures, a layer of vapor can form between the hot surface and the liquid. This is called film boiling. Heat doesn't transfer as well through this vapor layer.
Condensing Vapor
Condensation happens when a gas (vapor) cools down and turns into a liquid. When this happens, the gas releases latent heat. This is the same amount of heat that was absorbed when the liquid turned into a gas.
Here are some ways condensation can happen:
- Homogeneous condensation: This is like when fog forms in the air.
- Contact with a cold liquid: When vapor touches a cooler liquid.
- Contact with a cold surface: This is common in machines like heat exchangers.
- Filmwise condensation: A smooth layer of liquid forms on the cold surface. This happens when the liquid sticks to the surface.
- Dropwise condensation: Tiny drops of liquid form on the cold surface. This happens when the liquid doesn't stick to the surface.
- It's hard to keep dropwise condensation going reliably. So, most industrial equipment is designed for filmwise condensation.
Melting Solids
Melting is a process where a solid turns into a liquid. This happens when you add heat or pressure to a substance. Its temperature rises until it reaches its melting point. At this point, the particles in the solid break free from their fixed positions and start to move around more, turning into a liquid.
Most melted substances become less thick (less viscous) as they get hotter. However, there are exceptions, like the element sulfur, which actually gets thicker for a while before becoming thinner at even higher temperatures.
Images for kids
-
Simulation of heat moving in the Earth's mantle. Hot material rises, and cold material sinks.
-
Biochar is made by heating plant material without much air. This process helps store carbon and reduce heat in the atmosphere.
-
A traditional air cooler in Mirzapur, Uttar Pradesh, India.
See also
 In Spanish: Transferencia de calor para niños
In Spanish: Transferencia de calor para niños