History of Bosnia and Herzegovina facts for kids

Bosnia and Herzegovina is a country in Southeast Europe. Its history is long and full of changes. Long ago, this area was called Illyricum. It was home to ancient people called Illyrians.
Contents
Early History and Kingdoms
In the 1st and 2nd centuries A.D., the powerful Roman Empire took control of Illyricum. The Romans stayed until their empire fell apart in the 6th century. After the Romans, the Byzantine Empire ruled the area for a while. Later, parts of Bosnia became part of Hungary.
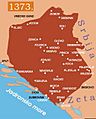
Around 1200 A.D., the people of Bosnia fought for their freedom from Hungary. They won and created their own Christian state. This state lasted for about 260 years.
Ottoman Rule and New Cultures
The Ottoman Empire grew very strong and moved into the Balkans. This brought new cultures and ways of life to Bosnia. The Ottomans defeated the Serbians in a big battle in 1389. They then conquered Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1463.
The Ottomans introduced Islam to the region. Many people became Muslim. Jewish people also moved to the capital city, Sarajevo. As the Ottoman Empire became smaller, so did its control over Bosnia.
Austria-Hungary and World War I
After a war between Russia and the Ottoman Empire, a meeting was held in Berlin in 1878. At this meeting, Austria-Hungary was given the right to govern Bosnia and Herzegovina. Bosnia was still officially part of the Ottoman Empire, but Austria-Hungary later fully took it over.
This made many Serbs unhappy. On June 18, 1914, a Serb nationalist assassinated the Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo. This event was one of the main causes of World War I. After the war, Bosnia and Herzegovina became part of a new kingdom called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. This kingdom later became known as Yugoslavia.
Yugoslavia and World War II
In 1941, Nazi Germany invaded Yugoslavia. Bosnia and Herzegovina became part of Nazi-controlled Croatia. Many Bosnians joined resistance fighters. They fought against the fascist troops in guerrilla battles.
After World War II ended, Bosnia and Herzegovina rejoined Yugoslavia. This time, Yugoslavia was under communist rule. Its leader was Marshall Tito.
Breakup of Yugoslavia and the Bosnian War
After Marshall Tito died, Yugoslavia's economy faced problems. The Berlin Wall fell in 1989, marking the end of communist rule in many parts of Eastern Europe. Yugoslavia began to break apart.
In December 1991, Bosnia declared its independence from Yugoslavia. They wanted to join the European Union. In 1992, the Bosnian president, Alija Izetbegovic, officially declared independence.
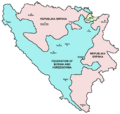
A war then started in Bosnia. Both Croatia and Serbia claimed parts of Bosnia. The United Nations stepped in to help. The United States helped set up peace talks in Dayton, Ohio. The war ended in 1995.
Modern Bosnia and Herzegovina
Today, Bosnia and Herzegovina is a democracy. It has a special three-part government. The country still faces challenges after the war. NATO helps keep the peace.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is now working to become a member of the European Union.
Images for kids
-
Illustration from the French magazine Le Petit Journal on the Bosnian Crisis: Bulgaria declares its independence and its prince Ferdinand is named Tsar, Austria-Hungary, in the person of Franz Joseph, annexes Bosnia and Herzegovina, while the Ottoman Sultan Abdul Hamid II looks on helplessly
-
Alija Izetbegović during his visit to the United States in 1997.
See also
 In Spanish: Historia de Bosnia y Herzegovina para niños
In Spanish: Historia de Bosnia y Herzegovina para niños