Index of color-related articles facts for kids
Colors are all around us! They make the world vibrant and exciting. From the bright blue sky to the green grass, colors help us understand and enjoy what we see. This article will explore what colors are, how we see them, and how they affect our lives.
What is Color?
Color is how our eyes and brain interpret different types of light. Light is made of waves, and each color has a different wavelength. When light hits an object, some colors are absorbed, and others are reflected. The colors that bounce off the object are the ones we see. For example, a red apple looks red because it reflects red light and absorbs other colors.
Seeing Colors
Our eyes have special cells called cones that detect color. We have three types of cones, each sensitive to red, green, or blue light. Our brain mixes the signals from these cones to create all the colors we see.
Color Blindness
Sometimes, a person's cones don't work perfectly. This can lead to color blindness, where they have trouble telling certain colors apart. The most common type is red-green color blindness. People with color blindness still see many colors, but some might look different to them.
Achromatic Colors
Not all colors are bright and colorful. Achromatic colors are those without any hue, like black, white, and grey. Black is what we see when no light is reflected. White is when all colors of light are reflected. Grey is a mix of black and white.
How We Make and Mix Colors
There are different ways to create and mix colors, depending on whether you are working with light or with pigments (like paint).
Primary Colors
The primary colors are the basic colors that cannot be made by mixing other colors. All other colors can be created by combining them.
Additive Primary Colors (Light)
When you mix light, you use additive primary colors: red, green, and blue (RGB).
- Mixing red and green light makes yellow.
- Mixing green and blue light makes cyan.
- Mixing red and blue light makes magenta.
- Mixing all three (red, green, and blue) light colors together creates white light.
This is how screens like TVs and phones create all their colors!
Subtractive Primary Colors (Pigments)
When you mix paints or inks, you use subtractive primary colors: cyan, magenta, and yellow (CMY). These are often used in color printing.
- Mixing cyan and yellow makes green.
- Mixing yellow and magenta makes red.
- Mixing cyan and magenta makes blue.
- Mixing all three (cyan, magenta, and yellow) pigments together creates black.
This is because pigments absorb certain colors of light, and when you mix them, they absorb more light, making the result darker.
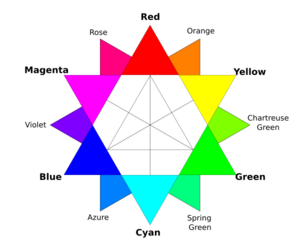
Secondary and Tertiary Colors
- Secondary colors are made by mixing two primary colors. For example, orange is a secondary color made from red and yellow.
- Tertiary colors are made by mixing a primary color with a secondary color next to it on the color wheel. An example is red-orange.
Complementary Colors
Complementary colors are pairs of colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel. For example, red and green are complementary. When placed next to each other, they make each other look brighter. When mixed, they can cancel each other out (especially with light) or create a dull color (with pigments).
Warm and Cool Colors
Colors can also be described as warm or cool.
- Warm colors like red, orange, and yellow often make us think of sunshine, fire, and warmth. They can feel energetic and exciting.
- Cool colors like blue, green, and purple remind us of water, sky, and nature. They can feel calm and peaceful.
Colors in Our World
Colors are important in many areas of life, from art to everyday objects.
Color Psychology
Color psychology studies how colors can affect our moods and feelings. For example:
- Blue often makes people feel calm or sad.
- Red can make people feel energetic or angry.
- Green often brings feelings of peace or nature.
- Yellow can make people feel happy or alert.
These feelings can change based on culture and personal experiences.
Color Symbolism
Colors often have special meanings or symbols in different cultures or situations.
- In many Western cultures, white symbolizes purity or peace.
- Black can symbolize mystery or formality.
- Red can symbolize love or danger.
These meanings are not always the same everywhere. For example, white is a color of mourning in some Eastern cultures.
Rainbows
A rainbow is a beautiful example of how light splits into its different colors. When sunlight passes through raindrops, the water acts like a prism, bending the light and separating it into the colors of the visible spectrum: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Color in Art and Design
Artists and designers use color theory to choose and combine colors effectively. They think about how colors will look together and what feelings they want to create. A color scheme is a plan for using colors in a design or artwork.
Color Photography
Before color photography, pictures were only in black and white. Now, cameras can capture all the amazing colors of the world. This lets us see photos that look much more like real life.
Lists
- List of colors: A–F
- List of colors: G–M
- List of colors: N–Z
- List of colors (compact)
- List of colors by shade
- List of color palettes
- List of color spaces
- List of Crayola crayon colors
- List of international auto racing colours
- List of RAL colors
- List of U.S. state colors
See also
- Lists of colors topics