Insular Region (Equatorial Guinea) facts for kids
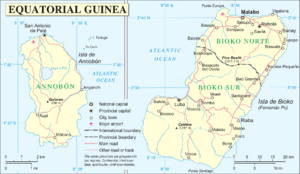
The Insular Region of Equatorial Guinea is a special part of this country. It's made up of two main islands: Bioko and Annobón. Long ago, these islands were controlled by Spain.
The region covers about 2,052 square kilometers (that's 792 square miles). In 2015, about 340,362 people lived there.
The biggest city in this region is Malabo. It's also the capital city of all of Equatorial Guinea! Other important cities include Luba, Riaba, Rebola, Baney, and San Antonio de Palé.
Meet the Islands
The Insular Region is divided into three areas, called provinces:
Some other islands, like those in Corisco Bay, are not part of the Insular Region. They belong to a different part of the country called the Continental Region.
Bioko Island
Bioko is the largest island in the Gulf of Guinea. It covers about 2,017 square kilometers (779 square miles). Until the 1970s, it was known by a different name: "Fernando Po."
Bioko is quite close to the country of Cameroon, only about 40 kilometers (25 miles) away.
Annobón Island
Annobón is a much smaller island, only about 17 square kilometers (6.6 square miles). It's a volcanic island, meaning it was formed by volcanoes!
Annobón is the most distant part of Equatorial Guinea. It's located about 670 kilometers (416 miles) from Malabo and 580 kilometers (360 miles) from another city called Bata. It's also just south of the equator, which is the imaginary line that goes around the middle of the Earth.
Between Annobón and Bioko, you'll find the country of São Tomé and Príncipe.
Want to Learn More?
 In Spanish: Islas de Guinea Ecuatorial para niños
In Spanish: Islas de Guinea Ecuatorial para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |