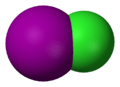Interhalogen facts for kids
An interhalogen is a special kind of chemical compound. It is made when two different halogen elements react and join together. Halogens are a group of elements found on the periodic table, like fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine.
Interhalogens are usually quite toxic and reactive, which means they can cause strong chemical reactions. Some examples you might hear about are chlorine trifluoride and bromine monochloride.
Contents
What are Halogens?
Halogens are a family of five non-metallic elements. They are found in Group 17 of the periodic table. The word "halogen" means "salt-forming" because these elements often form salts when they react with metals.
The main halogens are:
- Fluorine (F)
- Chlorine (Cl)
- Bromine (Br)
- Iodine (I)
- Astatine (At) - This one is radioactive and very rare.
Halogens are very reactive. This is because they only need one more electron to have a full outer shell, which makes them stable. So, they are always looking to grab an electron from another atom.
How Interhalogens Form
Interhalogens form when two different halogen atoms share electrons. This sharing creates a covalent bond. Because the two halogens are different, one will pull the shared electrons a bit more strongly than the other. This difference in "pulling power" (called electronegativity) makes the bond special.
The general formula for an interhalogen compound is XYn. Here, 'X' is the less electronegative (less electron-hungry) halogen, and 'Y' is the more electronegative (more electron-hungry) halogen. The 'n' can be 1, 3, 5, or 7. This number tells you how many 'Y' atoms are bonded to one 'X' atom.
Types of Interhalogens
Interhalogens can be classified based on how many atoms of the more electronegative halogen are attached to the less electronegative one.
XY Type
These are the simplest interhalogens. They have one atom of each halogen.
- Examples: Chlorine monofluoride (ClF), Bromine monochloride (BrCl), Iodine monochloride (ICl), Iodine monobromide (IBr).
- These compounds are often gases or liquids at room temperature.
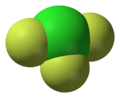
XY3 Type
These compounds have one atom of the less electronegative halogen and three atoms of the more electronegative halogen.
- Examples: Chlorine trifluoride (ClF3), Bromine trifluoride (BrF3), Iodine trichloride (ICl3).
- Chlorine trifluoride is a very strong oxidizing agent, meaning it can cause other substances to lose electrons easily. It's used in some industrial processes.
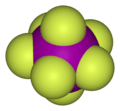
XY5 Type
These interhalogens have one atom of the less electronegative halogen and five atoms of the more electronegative halogen.
- Examples: Bromine pentafluoride (BrF5), Iodine pentafluoride (IF5).
- These are also very reactive and often used as fluorinating agents, which means they add fluorine atoms to other compounds.
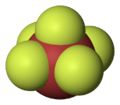
XY7 Type
These are the most complex interhalogens, with one atom of the less electronegative halogen and seven atoms of the more electronegative halogen.
- Example: Iodine heptafluoride (IF7).
- Iodine heptafluoride is a colorless gas and is also a strong fluorinating agent.
Properties and Uses
Interhalogens are generally very reactive and can be dangerous if not handled carefully. They are strong oxidizing agents. This means they can take electrons from other substances, causing chemical reactions.
Because of their high reactivity, interhalogens are used in some specific industrial applications. For example, some are used in the production of uranium for nuclear fuel, or as powerful fluorinating agents in chemical synthesis. They are also sometimes used in rocket fuels or as etching agents in the electronics industry.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Interhalógeno para niños
In Spanish: Interhalógeno para niños