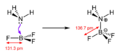Lewis acid facts for kids
The idea of Lewis acids and Lewis bases helps us understand how different chemicals react. It's a special way of looking at acids and bases that doesn't focus on protons (tiny parts of atoms). A scientist named Gilbert N. Lewis came up with this idea in the early 1900s.
In simple terms:
- A Lewis acid is a chemical that can accept and connect with a pair of electrons. Think of it as an electron "receiver."
- A Lewis base is a chemical that can give away a pair of electrons to form a connection. Think of it as an electron "donor."
When a Lewis acid and a Lewis base meet, they react together. They form a new compound called a Lewis adduct. This new compound is created when the Lewis base shares its electrons with the Lewis acid, forming a special type of covalent bond.
Contents
What are Lewis Acids?
Lewis acids are substances that are ready to accept a pair of electrons. They often have an empty space (an empty orbital) where these electrons can fit.
Examples of Lewis Acids
Many different types of chemicals can act as Lewis acids:
- Simple positive ions: Things like the silver ion (Ag+) or the copper ion (Cu2+). These ions are missing electrons and are eager to accept more.
- Molecules with incomplete electron shells: Some atoms in molecules don't have a full set of electrons around them. For example, in boron trifluoride (BF3), the boron atom only has six electrons around it, not the usual eight it "wants." So, it can accept two more electrons.
- Molecules with multiple bonds: Sometimes, a molecule with a double or triple bond can act as a Lewis acid if one of the atoms can temporarily shift its electrons to accept a new pair.
What are Lewis Bases?
Lewis bases are substances that have a pair of electrons they can share or "donate" to another chemical. These electrons are usually not involved in other bonds and are called "lone pairs."
Examples of Lewis Bases
Many common chemicals are Lewis bases:
- Water (H2O): The oxygen atom in water has two lone pairs of electrons it can share.
- Ammonia (NH3): The nitrogen atom in ammonia has one lone pair of electrons it can donate.
- Hydroxide ion (OH-): The oxygen atom in the hydroxide ion has several lone pairs and a negative charge, making it a strong electron donor.
- Halide ions: Ions like chloride (Cl-) or bromide (Br-) have extra electrons and can donate them.
How Lewis Acids and Bases React
When a Lewis acid and a Lewis base react, the Lewis base uses its available electron pair to form a new covalent bond with the Lewis acid. This new bond is often called a "dative bond" or "coordinate covalent bond" because both electrons in the bond come from only one of the atoms (the Lewis base).
For example, when ammonia (NH3, a Lewis base) reacts with boron trifluoride (BF3, a Lewis acid), the nitrogen in ammonia donates its lone pair of electrons to the boron in BF3. This forms a new compound, the ammonia-boron trifluoride adduct.
This idea of electron donation and acceptance is very important in many areas of chemistry, including how catalysts work and how different molecules fit together.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Teoría ácido-base de Lewis para niños
In Spanish: Teoría ácido-base de Lewis para niños