Maliki facts for kids
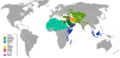
The Maliki (Arabic: مالكي) school is one of the four main ways of understanding Islamic law within Sunni Islam. It is the third-largest of these schools. About 15% of Muslims follow the Maliki school. Most of them live in North Africa and West Africa.
Contents
What is a Madhhab?
A madhhab is like a school of thought or a specific method for understanding Islamic law. These schools help Muslims know how to live according to their faith. They offer different ways to interpret the Quran and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad.
Who Started the Maliki School?
The Maliki school is named after its founder, Imam Malik ibn Anas. He was a very respected scholar who lived in the city of Medina in the 8th century. Medina was an important city because the Prophet Muhammad lived there. Imam Malik's teachings were based on the Quran, the Sunnah (Prophet Muhammad's practices), and the customs of the people of Medina.
Key Ideas of the Maliki School
The Maliki school gives special importance to the practices and traditions of the people of Medina. This is because Medina was the home of the Prophet Muhammad and his early followers. Maliki scholars also use common sense and public interest when making legal decisions. This helps them adapt Islamic law to new situations.
Where is the Maliki School Followed?
The Maliki school is most common in North Africa, including countries like Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya. It is also widely followed in West Africa, in countries such as Mali, Senegal, and Nigeria. You can also find followers in parts of the Arabian Peninsula.
Images for kids
-
The Great Mosque of Kairouan (also called the Mosque of Uqba or Mosque of Oqba) had the reputation, since the 9th century, of being one of the most important centers of the Maliki school. The Great Mosque of Kairouan is situated in the city of Kairouan in Tunisia.
See also
 In Spanish: Malikí para niños
In Spanish: Malikí para niños