Metallic bond facts for kids
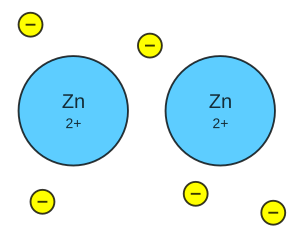
Imagine tiny building blocks called atoms. In metals, these atoms connect in a special way called a metallic bond. It's like a big team where many tiny particles called electrons are shared by many positive ions. These electrons act like a "glue" holding the metal together. This is different from covalent bonds or ionic bonds.
Metals have electrons that are easy to move. These electrons are not stuck to one atom. Instead, they float around like a "sea" or cloud of electrons. This "sea" surrounds all the metal atoms in a special structure.
Contents
Why Metals Are Strong and Shiny
The electrons and the positive ions in a metal pull strongly on each other. This strong pull is why metals often have high melting and boiling points. It's a bit like the strong forces in ionic bonds.
Metallic bonds give metals many of their special features. These include:
- Strength: Metals are usually very strong.
- Malleability: You can hammer metals into thin sheets without breaking them. Think of aluminum foil!
- Ductility: You can pull metals into long wires. Copper wires are a good example.
- Luster: Metals are shiny. This is because the free electrons can reflect light.
- Conduction of heat: Metals easily let heat pass through them.
- Electrical conductivity: Metals are good at carrying electricity.
How Metals Conduct Electricity and Heat
Metals can carry electricity because their electrons move freely. When you connect a metal to a power source, these free electrons quickly move. This creates an electric current.
Metals also conduct heat well for the same reason. The free electrons can quickly transfer heat energy from one part of the metal to another. This happens much faster than in materials where electrons are stuck in place.
Most non-metals do not conduct electricity. However, a few do. For example, graphite (a form of carbon) conducts electricity. This is because it also has free electrons, like metals. Also, some ionic compounds can conduct electricity if they are melted or dissolved in water. This is because their ions can move freely.
Understanding Metal Bonds
Metal atoms have at least one valence electron. These are electrons in the outermost energy level. In a metallic bond, these electrons are not shared with just one neighbor. They also don't completely leave to form ions. Instead, the outer energy levels of metal atoms overlap. This allows the electrons to move freely between many atoms. This is similar to how electrons are shared in covalent bonds.
Not all metals form metallic bonds in the same way. For example, mercury ions can form special covalent bonds with each other.
What Are Alloys?
An alloy is a mixture of two or more metals. Sometimes, it's a metal mixed with a non-metal. Most alloys are shiny, just like pure metals. A common example is steel, which is an alloy of iron and carbon. Alloys are often made to have better properties than pure metals. For example, they might be stronger or more resistant to rust.
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Enlace metálico para niños
In Spanish: Enlace metálico para niños

