Ionic compound facts for kids
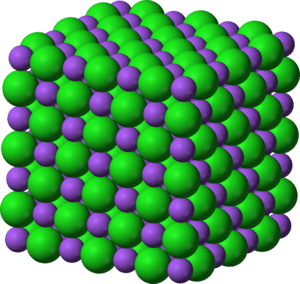
In chemistry, an ionic compound is a special kind of compound made from tiny charged particles called ions. Think of them like super strong magnets! These ions have very powerful connections called ionic bonds. Because these bonds are so strong, it takes a lot of energy (like heat) to break them apart. This is why ionic compounds usually have very high melting and boiling points.
Ions join together because they have different charges. One ion will have a positive charge, and another will have a negative charge. They are attracted to each other, just like opposite ends of a magnet. Ionic compounds often form when a metal atom and a non-metal atom come close together.
This happens when one atom gives an electron to another atom. Atoms want to have a full outer shell of electrons, just like the very stable noble gases. By giving or taking electrons, they become charged ions and can then form strong bonds.
How Ions Form
When atoms gain or lose electrons, they become ions.
- If an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positive ion (called a cation).
- If an atom gains electrons, it becomes a negative ion (called an anion).
Here's a simple way to think about it:
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 13 | Group 15 | Group 16 | Group 17 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example Element | Sodium (Na) | Magnesium (Mg) | Aluminum (Al) | Nitrogen (N) | Oxygen (O) | Chlorine (Cl) |
| Charge of Ion | 1+ | 2+ | 3+ | 3- | 2- | 1- |
| Symbol of Ion | Na+ | Mg2+ | Al3+ | N3- | O2- | Cl- |
Note: Elements in Group 14 (like carbon) usually share electrons instead of forming ions. Elements in Group 18 (like helium) are already stable and usually don't react to form ions.
What are the properties of Ionic Compounds?
Ionic compounds have some special features you can often observe:
| Property | What it means for Ionic Compounds |
|---|---|
| State at room temperature | They are usually solid crystals. Think of table salt! |
| Electrical conductivity |
|
| Boiling and Melting Point | They have very high boiling and melting points. It takes a lot of heat to break their strong bonds. |
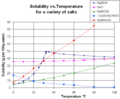
| Solubility in water | Many ionic compounds dissolve well in water. Water molecules can pull the ions apart. |
| Heat conductivity | They are usually poor conductors of heat. |
Images for kids
-
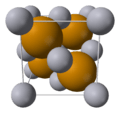
Halite, the mineral form of sodium chloride, forms when salty water evaporates leaving the ions behind.
-
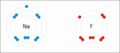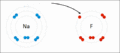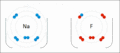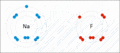
This picture shows how sodium and fluorine atoms can react to form sodium fluoride. Sodium loses an electron and fluorine gains it, making them charged ions that attract each other.
See also
 In Spanish: Sal (química) para niños
In Spanish: Sal (química) para niños