Miꞌkmaꞌki facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Miꞌkmaꞌki
|
|
|---|---|
| Pre-contact–1867 (as a State) 1867–Current (as an unrecognized country) |
|
|
Flag
|
|
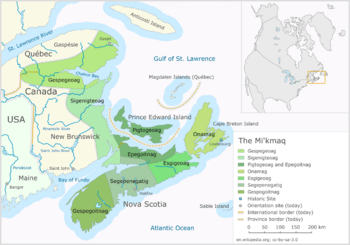
Seven Districts of Miꞌkmaꞌki excluding Taqamkuk
|
|
| Status | Confederated Districts of Wabanaki |
| Capital | Mniku, Unamaꞌkik |
| Common languages | Miꞌkmawiꞌsimk |
| Demonym(s) | Miꞌkmaq |
| Government | Santeꞌ Mawioꞌmi / Miꞌkmawey Mawioꞌmi |
| Kji Sagamaw | |
|
• unknown-1611
|
Henri Membertou |
|
• 1792-1818
|
Francis Peck |
|
• 1818-1842
|
Michael Tooma |
| Sagamaw | |
| Putus | |
| History | |
|
• Established
|
Pre-contact |
|
• Contact with John Cabot
|
1497 |
|
• Exclusion from the Treaty of Utrecht
|
1713 |
|
• First Treaty with Great Britain after the Anglo–Wabanaki War
|
1725 |
|
• Indian Act, 1876
|
1867 (as a State) 1867–Current (as an unrecognized country) |
| Population | |
|
• pre-1500
|
35,000-75,000 |
|
• 1500
|
4,500 |
|
• 1750
|
3,000 |
|
• 1900
|
4,000 |
|
• 2016
|
58,763 |
| Currency | Wabanaki Wampum |
| Today part of | Canada |
Miꞌkmaꞌki, also called Miꞌgmaꞌgi, is the traditional land of the Miꞌkmaq people. It includes their historic and current territories. This area is shared by different Miꞌkmaq First Nations groups.
Miꞌkmaꞌki is divided into seven main traditional areas. Today, Taqamkuk is also seen as an eighth district. Miꞌkmaꞌki is part of the larger Wabanaki group of nations.
Each district in Miꞌkmaꞌki used to be independent. It was led by a Sagamaw, or chief. These chiefs would meet with special people called Wampum readers. They also met with knowledge keepers, a women's council, and the Kji Sagamaw, or Grand Chief. Together, they formed the Santeꞌ' or Miꞌkmawey Mawioꞌmi (Grand Council). The main meeting place for the Grand Council is at Mniku. This place is in Unamaꞌkik and still serves as a capital today. It is located within the Potlotek reserve.
After Europeans arrived, France and Britain both tried to claim Miꞌkmaꞌki. This land is now part of modern Nova Scotia. The Miꞌkmaq people sided with the French. They fought alongside other Wabanaki warriors in many wars between France and Britain. These wars happened in North America from 1688 to 1763.
European powers later divided Miꞌkmaꞌki in treaties. These were the Treaty of Utrecht (1715) and the Treaty of Paris (1763). After the 1763 treaty, Britain claimed Miꞌkmaꞌki as its own. The Miꞌkmaq then signed Peace and Friendship Treaties with the British. These treaties aimed to end fighting and encourage working together. They also helped the Miꞌkmaq people survive. Their population had become very small due to diseases and hunger.
The power of Miꞌkmaꞌki lessened after Canada became a country in 1867. This event is known as the Confederation of Canada. The new country passed the Indian Act in 1876. This law meant that First Nations lost their independent ways of governing themselves. The Miꞌkmaq people have always said they never gave up control of their traditional lands. Some experts argue that the Peace and Friendship treaties allowed Britain to take over the land.
For over 100 years, until 2020, the Santeꞌ Mawioꞌmi (Grand Council) mainly focused on spiritual matters and discussions. Mi'kmaq and other First Nations had to elect their own government leaders. But in 2020, the Grand Council made an agreement with the Government of Canada. This agreement allowed the Grand Council to speak for all Miꞌkmaq First Nations. It also allowed them to speak for all First Nations in the province.
Miꞌkmaq Governance

In the past, each Mi'kmaw district had its own independent government. These governments had a chief and a council. The council included band chiefs, respected elders, and other important leaders.
The councils had many important jobs, just like any government. They could create laws and set up a justice system. They also divided the land for hunting and fishing among their people. They could decide to go to war or to seek peace.
The main Grand Council, called Santeꞌ Mawioꞌmi, brought these districts together. It was made up of the keptinaq (captains), who were the district chiefs. The Grand Council also included elders and putus. Putus were historians who read special Wampum belts. There was also a Council of women.
The Grand Council was led by a Grand Chief. This chief was usually one of the district chiefs, often the Unamaꞌkik chief. The position of Grand Chief was passed down through families. The main meeting place for the Grand Council was usually on Unamaꞌkik (Cape Breton Island).
Miꞌkmaq Districts
Miꞌkmaꞌki is divided into eight main districts. Here are their names, with two different spellings:
 | Jackie Robinson |
 | Jack Johnson |
 | Althea Gibson |
 | Arthur Ashe |
 | Muhammad Ali |