Molina's hog-nosed skunk facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Molina's hog-nosed skunk |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Mephitidae |
| Genus: | Conepatus |
| Species: |
C. chinga
|
| Binomial name | |
| Conepatus chinga (Molina, 1782)
|
|
 |
|
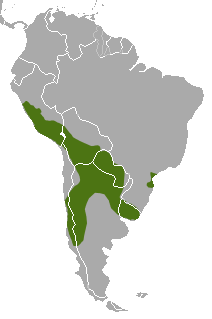
| Molina's hog-nosed skunk range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Molina's hog-nosed skunk, also known as the Andes skunk (Conepatus chinga), is a type of skunk found in South America. You can find these skunks in countries like Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Peru, Paraguay, and Uruguay. They live in places as high as 5,000 meters (about 16,400 feet) above sea level.
Contents
Where Do Molina's Hog-Nosed Skunks Live?
Molina's hog-nosed skunks live across the middle and southern parts of South America. This includes Chile, Peru, northern Argentina, Bolivia, Paraguay, Uruguay, and southern Brazil. They prefer areas with mild weather and open spaces. You'll often find them in grasslands called the Pampas. They also like open plants, bushy forests, and rocky hillsides.
How Many Skunks Are There?
These skunks usually live by themselves. An average area might have about 1.66 skunks per square kilometer. Sometimes their home areas overlap a little. About six skunks might live across an area of 3.5 square kilometers. Even though they mostly live alone, skunks will meet up for a short time when it's time to mate.
What Do Molina's Hog-Nosed Skunks Eat?
Molina's hog-nosed skunks mostly look for food at night. They are omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and animals. Their diet includes birds, small mammals, eggs, and insects. They also munch on leaves and fruits. Their teeth are special because they are very good at grinding food. This helps them eat all the different things in their diet.
Protecting Molina's Hog-Nosed Skunks
The Molina's hog-nosed skunk is listed as "least concern" by the IUCN Red List. This means they are not currently in danger of disappearing. However, they do face some threats. One big problem is that humans are changing or destroying their natural homes. This happens when land is used too much for farming or other human activities. New roads can also be dangerous for skunks, as they can get hit by cars. Because their natural homes are changing, some skunks have started living near human buildings, fences, and other structures.
See also
 In Spanish: Chingue para niños
In Spanish: Chingue para niños


