Mongolic languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Mongolic |
|
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution: |
Mongolia; Inner Mongolia and regions close to its border, Xinjiang, Gansu, Qinghai (China); Buryatia and Kalmykia (Russian Federation) |
| Linguistic classification: | Altaic (controversial)
|
| Subdivisions: |
Central Mongolic
Shirongolic
Dagur
|
| ISO 639-5: | xgn |
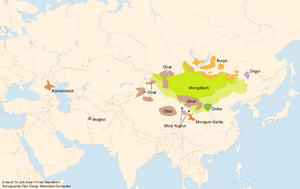 Geographic distribution of the Mongolic languages
|
|
The Mongolic languages are a group of languages spoken mainly in Central Asia. Imagine them as a family of languages that are related to each other. Some experts who study languages, called linguists, think that Mongolic languages might be part of an even bigger family. They suggest that Mongolic languages could be related to Turkic and Tungusic languages. This larger group is sometimes called the Altaic languages, but not all linguists agree on this idea.
Contents
What Are Mongolic Languages?
The Mongolic languages are a group of languages spoken by millions of people across Asia. They share similar grammar rules and words, much like how English, German, and Dutch are related in the Germanic language family.
Where Are Mongolic Languages Spoken?
These languages are mostly spoken in Mongolia, China (especially in Inner Mongolia), and parts of Russia. You can also find speakers in some areas close to these countries.
The Most Famous Mongolic Language
The most well-known language in this family is Mongolian. It's the main language for most people living in Mongolia. About 5.7 million people speak Mongolian across Mongolia, Russia, and China.
How Mongolian is Written
Mongolian can be written in different ways:
- In Mongolia, people use the Cyrillic alphabet. This is the same alphabet used for Russian. In Cyrillic, Mongolian is written as Монгол Хэл.
- In Inner Mongolia (a part of China), people use an older, vertical writing system. This script comes from the Uygur script. In this vertical script, Mongolian is written as Mongγol Kele.
See also

- In Spanish: Lenguas mongólicas para niños
Images for kids
 | Valerie Thomas |
 | Frederick McKinley Jones |
 | George Edward Alcorn Jr. |
 | Thomas Mensah |