Yautia madera facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Yautia madera |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Montrichardia
|
| Species: |
arborescens
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
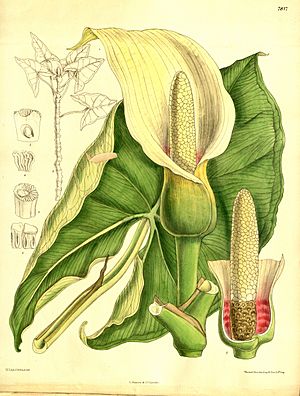
Montrichardia arborescens, also known as yautia madera or moco-moco, is a cool tropical plant. It grows along river banks, in swamps, or near creeks. This plant can reach a height of up to 9 feet!
Its leaves are shaped like arrows and provide food for many animals. The plant also produces flowers, which then turn into fruits. These fruits are edible and can be cooked. The plant's fruit clusters have about 80 tasty yellow fruits.
Contents
Where Moco-Moco Grows
You can find Montrichardia arborescens mostly in South America. It also grows in parts of the Caribbean and Mesoamerica. Some of the places where it lives include Puerto Rico, Panama, Guyana, Suriname, Venezuela, Brazil, and Colombia. This plant is originally from the tropical parts of the Americas and the West Indies.
Its Home and How It Lives
Montrichardia arborescens is a type of shrub that loves wet places. It grows best in bays and mangrove areas. You'll often see it along the edges of rivers, creeks, and in swamps. It can grow in salty water, slightly salty water, and fresh water.
This plant usually has a short life. It cannot handle cold temperatures very well. It grows best in full sun or with some shade. It can also grow in most types of soil. Like many plants in its family, it needs a lot of water. However, it can also survive short dry periods. People often grow this plant near ponds because it forms impressive groups.
What Moco-Moco Looks Like
The stem of the plant usually grows up to 3 meters (about 10 feet) tall. It often looks swollen at the bottom. The stem can be up to 25 cm (about 10 inches) wide. Sometimes, it even has small prickles.
The leaf stalks can be up to 30 cm (about 12 inches) long. The leaf blades are usually 10–30 cm (4–12 inches) long. They have a clear triangular shape, with special lobes at the base. The flower part of Montrichardia arborescens is shaped like a cylinder or an oval when it's fully grown. The seeds of this plant usually float to the shore and then start to grow.
Flowers and Fruits
The flowers of M. arborescens grow on a special spike called a spadix. This is common for plants in the Araceae family. The spadix has small flowers packed closely together on a fleshy stem.
The spadix has separate male and female flowers. The female flowers are at the bottom of the flower cluster. The male flowers are at the top. There are also some undeveloped flowers between the male and female parts. Studies have shown that the pollen from M. arborescens grows pollen tubes very quickly. This quick growth helps the plant reproduce. The plant's seeds float and germinate, helping new plants to grow.
How People Use Moco-Moco
As Food
The fruit cluster of Montrichardia arborescens is edible. You can cook or toast the seeds. Plants like M. arborescens have been an important food source for many people in tropical areas for a long time. They can provide lots of healthy food.
For Medicine
In Suriname, people use the milky liquid from the stem to help treat deep cuts. At first, people thought this sap could cause skin irritation. But later, they found it could also be used for nosebleeds and sore eyes. The sap can also be put on skin sores as a poultice. Dried roots and leaves can be used to help with high blood pressure.
Other Cool Uses
Montrichardia arborescens has other interesting uses too! The strong fibers from the stem can be used to make cords or ropes. The berries and fruit spikes can be used as bait for fishing. The soft tissue inside the stem can even be used to make paper.
Other Names for Moco-Moco
- Aninga
- Arracacho
- Arum lily
- Fruit of the devil
- Malanga-gratter
- Moco moco / Moko moko / Mokumoku / Mocou mocou
- Yautia-madera
See also
 In Spanish: Arracacho para niños
In Spanish: Arracacho para niños