Northern Rocky Mountain Intermontane Basins Aquifer System facts for kids
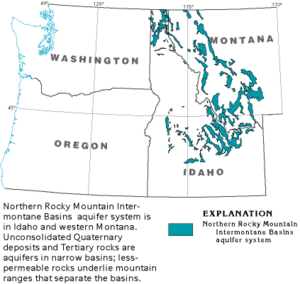
The Northern Rocky Mountain Intermontane Basins aquifer system is a huge underground water supply. It's mostly made of loose sand and gravel. You can find it under parts of western Montana, Idaho, and a small bit of Washington. These underground water areas, called aquifers, are not all connected like one big lake. Instead, they are narrow areas of sand and gravel left behind by ancient glaciers. They all share a similar geological past.
Contents
What Are These Aquifers Like?
These aquifers are found in large, bowl-shaped areas called basins. These basins are filled with layers of sand and gravel that are not packed together very tightly. These layers can be as thick as 16,000 feet (about 3 miles!). Hard rock, called bedrock, separates these basins.
Types of Aquifers in the Region
The sand and gravel aquifers here are usually close to the surface. They are often small and not fully mapped out. There are four main types of these aquifers:
- Valley-fill aquifers: Found in valleys.
- Blanket sand and gravel aquifers: Spread out like a blanket.
- Glacial-deposit aquifers: Formed from material left by glaciers.
- Stream-valley aquifers: Found along stream valleys.
This region covers about 80,000 square miles and has 70 different watersheds (areas where all water drains to a common point). The sand and gravel left by rivers and glaciers in this area are known for holding a lot of water.
Why Are These Aquifers Important?
These aquifers are very important because many people rely on them for their daily water needs.
Risk of Pollution
Because these aquifers are close to the surface, they are at a high risk of getting polluted. Water can easily flow through the sand and gravel, carrying pollutants with it.
- Mining pollution: Past mining activities have left harmful substances like arsenic, cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc in the ground. These can seep into the water.
- Farm pollution: Agricultural activities can add high levels of phosphorus and nitrogen to the water. These come from fertilizers and animal waste.
Water Use in the Region
Most of the water used in this region (about 80%) comes from surface water, like rivers and lakes. Only about 20% comes from groundwater. However, for homes, businesses, and cities, about 60% of their drinking water comes from these underground aquifers.
Wells that tap into these aquifers can be anywhere from 50 to 1,125 feet deep. Even though this part of the United States isn't heavily populated, more than half the people living here depend on these aquifers for their drinking water. This makes protecting them from pollution very important.