Nottaway River facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Nottaway |
|
|---|---|
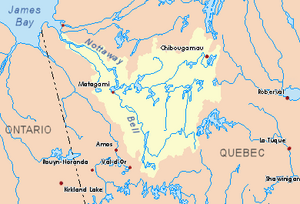
Nottaway River basin in yellow
|
|
| Country | Canada |
| Province | Quebec |
| Region | Jamésie |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | Lake Matagami Matagami 50°03′00″N 77°28′10″W / 50.05000°N 77.46944°W |
| River mouth | Rupert Bay off James Bay About 17 km SW of Waskaganish 0 m (0 ft) 51°23′30″N 78°48′00″W / 51.39167°N 78.80000°W |
| Length | 200.2 km (124.4 mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 65,800 km2 (25,400 sq mi) |
| Tributaries |
|
The Nottaway River is an important river located in Quebec, Canada. It starts from Lake Matagami and flows about 225 kilometers (140 mi) northwest. The river then empties into Rupert Bay, which is at the southern end of James Bay.
The area of land that drains into the Nottaway River is called its drainage basin. This basin covers a huge area of 65,800 square kilometers (25,400 sq mi). The river carries a large amount of water, with an average flow of 1190 cubic meters per second. The very beginning of the river's system is the Mégiscane River, which is 776 kilometers (482 mi) away from where the Nottaway meets the bay.
Two significant lakes along the Nottaway River are Soscumica Lake (50°15′N 77°27′W / 50.250°N 77.450°W) and Dusaux Lake (50°45′00″N 77°53′30″W / 50.75000°N 77.89167°W).
The Nottaway River was once considered for a big hydro-electric project. This project, called the James Bay Project, aimed to build dams and generate electricity. However, in 1972, the focus shifted to other rivers further north, like the La Grande and Eastmain Rivers. Because of this, the Nottaway River was not developed for power. It's unlikely to be developed in the near future, especially since the Rupert River's water is now being sent to the La Grande River.
Contents
Exploring the Nottaway River's Geography
The Nottaway River's name refers to the lower part of Lake Matagami. The river itself is about 200.2 kilometres (124.4 mi) long. However, if you include its source, the Mégiscane River, the entire waterway stretches for 776 kilometres (482 mi). This long river flows through many lakes on its way northwest.
From Lake Matagami, the Nottaway River forms lakes like Soscumica and Dusaux. It also collects water from several other rivers, including the Kitchigama River. Finally, it reaches Rupert Bay at the southern end of James Bay. This is located west of the Broadback River and Rupert River.
The river's drainage basin is 65,800 square kilometres (25,400 sq mi), and its average water flow is 1,190 cubic metres per second (42,000 cu ft/s). The Nottaway River flows through many marshy areas, especially closer to its mouth.
The mouth of Lake Matagami is located:
- 32.2 kilometres (20.0 mi) north of downtown Matagami.
- 159.5 kilometres (99.1 mi) south of where the Nottaway River meets Rupert Bay.
- 114.7 kilometres (71.3 mi) northwest of the village of Lebel-sur-Quévillon, Quebec.
From the mouth of Lake Matagami, the Nottaway River flows for 200.2 kilometres (124.4 mi). This journey can be divided into two main parts:
Upper Nottaway River Journey
This upper section of the Nottaway River is about 93.1 kilometres (57.8 mi) long.
- For the first 13.4 kilometres (8.3 mi), it flows north, crossing the southern part of Soscumica Lake. It also collects water from the "Lac de la Tourbière."
- Then, for 37.4 kilometres (23.2 mi), it flows north and then west, going through the entire length of Soscumica Lake (which is at an altitude of 242.1 metres (794 ft)). In this part, it collects water from the Natchiowatchouan River.
- Next, for 27.2 kilometres (16.9 mi), it flows northwest. It gathers water from lakes like Kawawiyekamach and Mistatikamekw. This section leads to the "Rapides des Taureaux" (Bulls Rapids).
- Finally, for 15.1 kilometres (9.4 mi), it flows north, going around Kauskatistin Island and through the Longs Rapides. This part ends at "Iroquois Falls," which is at the entrance of Dusaux Lake.
Lower Nottaway River Journey
The lower part of the Nottaway River is about 107.1 kilometres (66.5 mi) long.
- It flows northwest for 20.7 kilometres (12.9 mi), crossing all of Dusaux Lake (at 200 metres (660 ft) altitude). Here, it collects the Davoust River and flows past Nestipuku Island and Michikushish Island, reaching Vandry Island.
- For the next 18.7 kilometres (11.6 mi), it flows northwest, first going around Vandry Island, until it reaches Interdite Island.
- Over 21.3 kilometres (13.2 mi), it collects water from the Richerville River and the Iroquois River. This section narrows down.
- Then, for 11.9 kilometres (7.4 mi), it continues northwest until it meets the Kitchigama River.
- For 16.7 kilometres (10.4 mi), it flows northwest, passing two large islands, including D'Herbomez Island. The river then widens, with rapids and many small islands.
- The final 17.8 kilometres (11.1 mi) of the river flows northwest, going past Kakupanchish Island, Lavoie Island, and Lemoine Island, until it reaches its mouth.
The mouth of the Nottaway River is located:
- 179.6 kilometres (111.6 mi) northwest of downtown Matagami.
- 33.9 kilometres (21.1 mi) south of the village of Waskaganish (Cree village municipality).
- 91.2 kilometres (56.7 mi) southeast of Charlton Island in James Bay.
Main Islands of the Nottaway River
(Listed from the mouth upstream) Lemoine Island, Lavoie Island, Kakupanchish Island, Kaminahikushach Island, Misiministikw Island, D'Herbomez Island, Des Sept Miles Island, Interdite Island (Bras Kapakusipastikuch), Vandry Island (Bras Spipastikw), Desmolier Island, Michikushish Island, Nestipuku Island, Kauskatistin Island.
Main Rapids of the Nottaway River
(Listed from the mouth upstream) Rapides Kanutinitunanuch, rapides Kasischischiskasich, rapides Kaikunapischechuch, rapides Kachechekuch, Iroquois Falls, rapides Longs, rapides des Taureaux.
Major Rivers Joining the Nottaway
Some of the main rivers that flow into the Nottaway River include:
- Kitchigama River
- Lake Matagami (which itself has several rivers flowing into it):
The Meaning Behind the Nottaway River's Name
In the 1600s, the Iroquois people moved into the land of the Algonquin tribes near James Bay, along this river. When European mapmakers began drawing maps of the area in the late 1600s, they often called it "Rivière des Iroquois" (Iroquois River). You can see this name on old maps from 1699, 1703, and 1744.
However, different versions of the name "Nottaway" started to appear in the early 1700s. Some maps showed "Noddaways" in 1715, "Nodaway" in 1743, and "Nodaoay" or "Nodway" in 1744. Later, geologists used "Notaway River" in their reports. The spelling we use today, "Nottaway," became common in the early 1900s.
It's believed that the name "Nottaway" comes from the Algonquin word nadowe. This word means "snake." The Algonquin tribes used "snake" to describe their enemies, including the Iroquois. The Cree people called this river Natuweu Nipi, and the Iroquois themselves called it Nottaweou.
See also
 In Spanish: Río Nottaway para niños
In Spanish: Río Nottaway para niños

