Numic languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Numic |
|
|---|---|
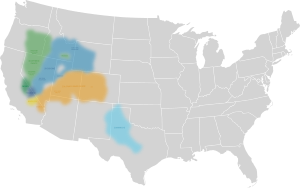
| Geographic distribution: |
Western United States |
| Linguistic classification: | Uto-Aztecan
|
| Subdivisions: |
Western Numic
Central Numic
Southern Numic
|
 |
|
Numic is a group of seven languages. They are part of the larger Uto-Aztecan language family. Native American peoples traditionally speak these languages. They live in areas like the Great Basin, Colorado River basin, Snake River basin, and southern Great Plains.
The word "Numic" comes from a similar word in all these languages. This word means "person." For example, in many Central and Western Numic languages, it sounds like /nɨmɨ/. In Kawaiisu and Colorado River languages, it sounds like /nɨwɨ/, /nɨŋwɨ/, or /nuu/.
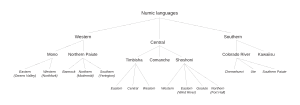
Numic Language Groups
Numic languages are divided into three main groups:
- Central Numic languages
- Southern Numic languages
- Kawaiisu
- Colorado River (includes Chemehuevi, Southern Paiute, and Ute)
- Western Numic languages
- Mono (with Eastern and Western dialects)
- Northern Paiute (with different regional ways of speaking)
Most of these groups have one language spoken in a small area. This area is usually in the southern Sierra Nevada mountains and nearby valleys. Examples are Mono, Timbisha, and Kawaiisu. Each group also has a language spoken over a much larger area. These include Northern Paiute, Shoshoni, and Colorado River.
How Numic Languages Spread
This pattern suggests that Numic-speaking people spread out from a small area. This likely happened quite recently. This original area might have been near the Owens Valley. Studies of words and other scientific research support this idea.
For example, the Comanche people split from the main Shoshoni group. This happened in the late 1600s or early 1700s. They moved southeast onto the Great Plains. Over time, their Shoshoni way of speaking changed. This eventually became the Comanche language. Comanche and Shoshoni are still quite similar. However, some sound changes in Comanche make it hard for speakers of one language to understand the other.
See also
 In Spanish: Lenguas númicas para niños
In Spanish: Lenguas númicas para niños