Orthodera novaezealandiae facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Orthodera novaezealandiae |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Mantodea |
| Family: | Mantidae |
| Genus: | Orthodera |
| Species: |
O. novaezealandiae
|
| Binomial name | |
| Orthodera novaezealandiae (Colenso, 1882)
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Orthodera novaezealandiae, also known as the New Zealand mantis or the New Zealand praying mantis, is a type of praying mantis. As its names suggest, this insect is naturally found only in New Zealand. It is an endemic species, meaning it lives nowhere else in the world.
Contents
What Does It Look Like?
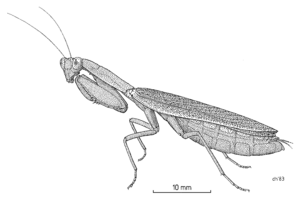
When they are young, New Zealand mantises are called nymphs. They are pale, see-through green. They have a dark stripe that runs from their head all the way to the end of their body.
As adults, these mantises are bright green. They grow to be about 35 to 40 millimeters long. That's about 1.4 to 1.6 inches. Like many mantis species, the female is usually bigger than the male. This difference in size between males and females is called sexual dimorphism.
The New Zealand mantis has a head shaped like a triangle. Its compound eyes are a bit large. These eyes give it excellent binocular vision, which means it can see depth well. However, it does have a small blind spot.
This mantis is a very active hunter. Its front legs are special. They are long and have very sharp spikes. These spikes help the mantis catch and hold its prey. You can tell this mantis apart from another species, Miomantis caffra, by looking at its forelegs. The New Zealand mantis has blue eyespots on the underside of its front legs. Miomantis caffra is a species that came from South Africa and settled in New Zealand in the 1970s.
Where Do They Live and What Do They Eat?
New Zealand mantises like to live in open areas with lots of shrubs. Their bright green color helps them blend in with leafy vegetation. This is a type of camouflage. They use this camouflage to hide and then suddenly attack their prey.
You can find many of them in small manuka and kanuka trees. These trees grow in open, grassy places. In these areas, there are many small insects like moths for them to eat.
The New Zealand mantis is very good at hiding from animals that might want to eat it. It is also near the top of the invertebrate food chain in its habitat. This means it eats many other insects. Since it is an endemic species to New Zealand and eats many pest insects, it is helpful to farmers and gardeners. They are known as a beneficial insect.
However, New Zealand mantises can be harmed by pesticides. Pesticides can kill them directly or reduce the number of insects they eat. Their egg cases can also be attacked by tiny parasitic wasps. Male New Zealand mantises are sometimes attracted to females of the introduced M. caffra species. This can be dangerous for the male New Zealand mantis.
There are only two types of mantises in New Zealand. One is this native species, O. novaezealandiae. The other is the introduced species, M. caffra. M. caffra was first found in the Auckland suburb of New Lynn in 1978.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
Female mantises lay their eggs in a special case called an ootheca. The eggs of the New Zealand mantis are neatly arranged in two rows inside the ootheca. This is different from the more jumbled egg mass of Miomantis caffra.
Mantises often place their oothecae on the warm sides of branches and tree trunks. They usually face north towards the sun.
Keeping Them as Pets
People sometimes keep New Zealand mantises as pets. If you keep them, you need to be careful. This species is small and moves very quickly. Young mantises, or nymphs, are especially fast. They can also jump quite far.
You can keep them at room temperature, around 25 to 30 degrees Celsius (77 to 86 degrees Fahrenheit). They do prefer warmer temperatures. Their enclosure should be sprayed with water a few times a week. When they are young, their home should have about 50% to 60% humidity.
New Zealand mantises kept in captivity can eat small crickets and flies. Young nymphs can easily be fed small fruit flies.
See also
 In Spanish: Orthodera novaezealandiae para niños
In Spanish: Orthodera novaezealandiae para niños
 | Aaron Henry |
 | T. R. M. Howard |
 | Jesse Jackson |