Overseas departments of France facts for kids
France has special areas called overseas departments. These are like regular parts of France, but they are located far away from the main country in Europe. They are official parts of France, just like any department you'd find in Europe. This makes them different from "overseas territories," which have a slightly different status.
These overseas departments are also part of the European Union and use the Euro currency, just like France itself.
Contents
What are France's Overseas Departments?
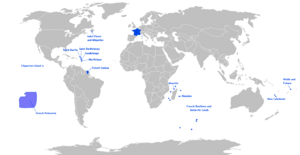
France currently has five overseas departments. Since 2003, they are also officially called "overseas regions." However, most people still use the older name, "overseas departments."
Each of these regions sends elected representatives to the French government in Paris. They have members in the Senate and the National Assembly. These are the two main parts of France's parliament. Three members are also elected to the European Parliament to represent all of overseas France.
Since 1974, these regions have had their own local governments. These are called regional councils. They help manage things like schools, roads, and local development.
Where are France's Overseas Departments Located?
France's overseas departments are spread across different parts of the world. They are located in South America, the Caribbean, and Africa.
Here is a list of the current overseas departments:
| Flag | Department | Main City | Region | Became a Department | How it Became a Department |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| French Guiana (French: Guyane) |
Cayenne | South America | 19 March 1946 | By a decision of the parliament | |
| Guadeloupe (French: Guadeloupe) |
Basse-Terre | Caribbean | 19 March 1946 | By a decision of the parliament | |
| Martinique (French: Martinique) |
Fort-de-France | Caribbean | 19 March 1946 | By a decision of the parliament | |
| Mayotte (French: Mayotte) |
Mamoudzou | Africa | 31 March 2011 | After a public vote (Referendum) | |
| Réunion (French: La Réunion) |
Saint-Denis | Africa | 19 March 1946 | By a decision of the parliament |
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Departamento y región de ultramar para niños
In Spanish: Departamento y región de ultramar para niños
 | Madam C. J. Walker |
 | Janet Emerson Bashen |
 | Annie Turnbo Malone |
 | Maggie L. Walker |