Photocatalysis facts for kids

Photocatalysis is a cool way to make chemical reactions happen faster using light. Think of light as a special helper, or a catalyst, that speeds things up!
Many reactions that use light start when light creates something called a free radical. Light carries a lot of energy, enough to break apart chemical bonds. This is why things like clothes or pictures can fade if left in the sun for too long. When light breaks these bonds, free radicals are made.
A free radical is like a tiny, hungry particle (a molecule, atom, or ion) that really wants an electron. It will grab electrons from other molecules or atoms, and this is what kicks off a chemical reaction.
Contents
What Do These Words Mean?
- Photo: This word always means that light is involved.
- Photolysis: This is when light "cuts" or breaks the bonds of a molecule.
- Reactants: These are the ingredients you start with in a chemical reaction.
- Products: These are what you get after the reaction is finished.
For example, when methane gas (CH4) burns with oxygen (O2), methane and oxygen are the reactants. They turn into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), which are the products.
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
How Catalysts Help Reactions
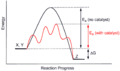
A catalyst is a special substance that helps a chemical reaction go faster without being used up itself. Imagine a hill that a reaction needs to climb to get from reactants to products. This hill is called the activation energy (Ea).
A catalyst makes this hill smaller, so the reaction needs less energy to happen. For instance, when you light methane gas, you give it the energy it needs to start burning. A catalyst would make it easier for the methane to start burning.
Speeding Up Reactions
The rate of a reaction tells us how fast or slow a chemical change happens. A catalyst helps to increase this rate.
Look at the graph below. The black line shows a reaction without a catalyst; it has a higher "energy hill" to get over. The red line shows the same reaction with a catalyst. See how the "energy hill" is much lower? This means the reaction can happen more easily and quickly.
All About Light
Light is super fast! In an empty space (a vacuum), light travels at about 299,792,458 meters per second. That's about 186,000 miles in just one second!
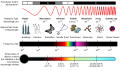
We often show light as a wavy pattern. The highest points of the wave are called crests, and the lowest points are called troughs. We describe light using three main features:
- Wavelength (λ): This is the distance between two crests that are right next to each other.
- Frequency (ν): This is how many waves pass by a certain point in a specific amount of time.
- Amplitude: This is the height of the wave, measured from the middle line to a crest or a trough.
Amazing Uses of Photocatalysis
Scientists are very interested in photocatalysis, especially because of the "green movement" – the effort to protect our planet.
One exciting area of research is trying to copy photosynthesis. This is the amazing process plants use to make their own food (sugar). Plants take carbon dioxide gas from the air, water, and sunlight, and turn them into food. Plants have a special molecule that helps them do this.
Scientists hope to create similar molecules that can make useful products, like fuels, just by using carbon dioxide from the air, water, and light. If we could do this, it would greatly reduce pollution because we would be using carbon dioxide that's already in the air to make fuel!
See also
 In Spanish: Fotocatálisis para niños
In Spanish: Fotocatálisis para niños