Pyramid of the Moon facts for kids

Pyramid of the Moon
|
|
| Location | Mexico State |
|---|---|
| Region | Mesoamerica |
| Type | Pyramid, Temple |
| Part of | Teotihuacan |
| History | |
| Periods | Mesoamerican classic |
| Cultures | Teotihuacan |
| Site notes | |
| Condition | Protected by UNESCO |
| Ownership | Cultural heritage |
| Management | World Heritage Committee |
| Public access | Yes |
The Pyramid of the Moon is the second-largest pyramid in Mesoamerica. It is smaller than the Pyramid of the Sun. You can find it in modern-day San Martín de las Pirámides, Mexico.
This pyramid is in the western part of the ancient city of Teotihuacan. It looks like the mountain Cerro Gordo, which is just north of the city. People think Cerro Gordo might have been called Tenan, meaning "mother or protective stone" in the Nahuatl language. The Pyramid of the Moon was built over an older structure. This older part existed even before the year 200 AD.
The pyramid was built between 100 and 450 AD. It helped complete the balanced design of the temple area. The pyramid sits at the end of the Avenue of the Dead. A staircase connects it to the avenue. People used the pyramid for special ceremonies. They would offer animals and sometimes humans as sacrifices there. It was also a burial place for these offerings. These burials helped make each new layer of the pyramid seem more important. The pyramid grew bigger very quickly between 250 and 400 AD. This happened as new leaders came and ideas changed.
At the top of the pyramid, there was a platform. This platform was used for ceremonies honoring the Great Goddess of Teotihuacan. She was a very important goddess of water, growing things, the earth, and even creation. Both this platform and a sculpture at the pyramid's base are dedicated to her.
Across from the Great Goddess's altar is the Plaza of the Moon. This plaza has a central altar. It also has an old building with four parts that form what is called the "Teotihuacan Cross."
Contents
Discovering the Pyramid's Secrets
Between 150 BC and 500 AD, a Mesoamerican culture built a large city. This city was about 22 square kilometers (8.5 square miles) big. We don't know exactly what ethnic group lived in Teotihuacan. So, "Teotihuacan" is the name we use for both the civilization and its main city.
Teotihuacan was a very important civilization in Mesoamerica. The city had a religious center that was important for the whole region. The people built their city to fit their religious beliefs. They planned the city based on how they saw the universe.
During the early time of Teotihuacan (0–150 AD), clever building methods were used. These methods helped build the huge bases for the Pyramids of the Moon and the Sun. The city of Teotihuacan was well-planned. It had main roads and a large palace surrounded by 15 big pyramids. The Aztecs later said that a huge stone statue related to the moon was on top of the Pyramid of the Moon. This statue was found. It weighed 22 metric tons and was somehow lifted to the top. It shows the Great Goddess as a water deity.
Starting in 1998, archaeologists began digging under the Pyramid of the Moon. They dug Tunnels into the pyramid. These tunnels showed that the pyramid was rebuilt at least six times. Each new part was larger and covered the one before it.
As archaeologists dug through the pyramid's layers, they found many artifacts. These items help us understand the history of Teotihuacan. In 1999, a team led by Saburo Sugiyama and Ruben Cabrera found a tomb. It seemed to be for the fifth building phase. It held four human skeletons, animal bones, jewelry, obsidian blades, and many other offerings. Archaeologists think this burial happened between 100 and 200 AD.
Another tomb was found in 1998. It was also dedicated to The Great Goddess. This tomb was from the fourth building phase. It contained one human male who was sacrificed. It also had skeletons of a wolf, jaguar, puma, snake, and bird. Plus, there were over 400 other items. These included large greenstone and obsidian figures, ceremonial knives, and spear points.
How the Pyramid Looks
Pyramid Shape and Size
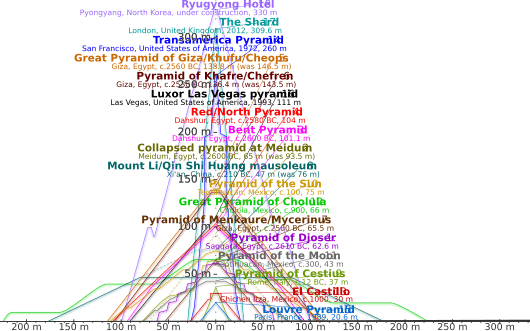
The Pyramid of the Moon looks like many other pyramids in Mesoamerica. The outside of the pyramid, which you can see today, has a special shape called talud-tablero. It has 7 layers of buildings built on top of each other. The pyramid is 43 meters (141 feet) tall. Its base is about 147 meters (482 feet) from west to east and 130 meters (426 feet) from north to south.
Because of its name and what was found inside, people think the pyramid's moon symbolism might be linked to water, the rainy season, women, fertility, and the earth.
Where the Pyramid is Placed
Many Mesoamerican cultures planned their cities to show their beliefs about the universe. The way the Pyramid of the Moon is placed tells us a lot about Teotihuacan.
The Pyramid of the Moon was placed carefully at the end of the Avenue of the Dead. It sits at the foot of Cerro Gordo mountain. This central spot makes it clear that the Avenue of the Dead was used for important processions. Many Mesoamerican temples were built to look like natural features. The connection between the mountain, the pyramid, and the road might show a link between the road and the underworld (a watery place). The mountain might have been seen as an anchor to the earth.
The way all the buildings in the city are lined up is also important. The city's north-south line shows its beliefs about the stars and the universe. This line was connected to their special 260-day calendar. The east-west line was for the city's everyday structure and to make it look balanced. A public plaza is at the base of the pyramid, connecting it to the Avenue of the Dead. This plaza was seen as a sacred place for rituals. The pyramid was built on top of it.
Building Layers Over Time
This pyramid has 7 different layers of buildings. Each new layer was built on top of the last one. This was done to make the building's religious power stronger over time.
- Building 1: This is the oldest part of the pyramid, from about 100 CE. It was a square platform with sloped sides (talud style) about 23.5 meters (77 feet) long.
- Building 2: This was a small addition that covered the first building. It also fixed the pyramid's direction slightly to line up better with the true east-west axis. It was also in the talud style.
- Building 3: This layer covered the one before it but didn't make the pyramid much bigger.
- Building 4: This was a much bigger addition. The pyramid became 89.2 meters (292 feet) wide from east to west and 88.9 meters (291 feet) long from north to south. This building was finished around 250 CE.
- Building 5: This layer was a bit bigger, but the main change was its building style. The east-west size stayed the same, but the north-south wall grew to 104 meters (341 feet). It used the talud-tablero style. This design still meant the pyramid was a stage for rituals, not a house for a temple.
- Building 6: This building grew to be 144 meters (472 feet) from east to west. It was built to hold Burials 5 and 4 around 350 CE.
- Building 7: This is the final structure you can see today. It was built around 400 CE. The different building styles in the first three layers might show that people's beliefs changed over time.
What the Pyramid Was Used For
More Than Just Sacrifices
The pyramid was used for other rituals besides offerings. In Mesoamerican cities, plazas were important for social life. The public plaza at the Pyramid of the Moon was also used to watch the stars and for activities related to the calendar.
The area around the pyramid had smaller pyramid structures, rooms, porches, patios, hallways, and low platforms. The Moon Plaza was a very important place for ceremonies, politics, and trade for the whole region.
Archaeologists have looked at the different layers of the pyramid. They found many artifacts and remains. Some of these can even be shown to the public. The artifacts found were made of greenstone, obsidian, and ceramic. All of these were carefully made in Teotihuacan. These items included small figures and serpent knives.
See also
 In Spanish: Pirámide de la Luna para niños
In Spanish: Pirámide de la Luna para niños
 | Roy Wilkins |
 | John Lewis |
 | Linda Carol Brown |