Quantum state facts for kids
The quantum state of something is like a special instruction manual for tiny particles. It's a way to describe everything we can possibly measure about something very small, like an atom or an electron.
Imagine you have a hydrogen atom. Its quantum state holds all the important details about it. This includes things like where it is, how fast it's moving (its momentum), how much energy it has, how it's spinning (its angular momentum and spin), and more. It tells us all the possible outcomes if we were to measure these properties.
Contents
What is a Quantum State?
A quantum state is a mathematical way to describe the condition of a quantum system. A quantum system is just a fancy name for very small things. These can be tiny particles like electrons, or even small groups of atoms.
This description tells us all the possible results we might get if we measure something about the particle. It also tells us how likely each of those results is. It's different from how we describe bigger objects. For example, a baseball has a clear position and speed at any moment. But a tiny electron doesn't work that way.
Why Do We Need Quantum States?
For everyday objects, like a car, we can easily know its exact speed and location at the same time. But in the quantum world, things are much stranger. Particles don't always have a single, definite position or speed until we measure them.
The quantum state helps us understand this strange behavior. It lets scientists predict what will happen when they experiment with these tiny particles. It's a fundamental idea in quantum mechanics, which is the science of the very small.
How Do We Describe a Quantum State?
Scientists use special mathematical tools to write down a quantum state. These tools often involve complex numbers and equations. Don't worry, you don't need to understand the deep math right now!
Think of it like a recipe. The recipe (the quantum state) tells you all the ingredients (properties like energy, spin) and how to combine them. When you "cook" (measure) the particle, you get a specific outcome.
Examples of Quantum States
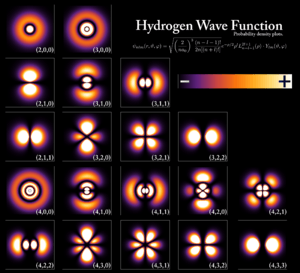
- Electron in an atom: The electrons orbiting an atom are in specific quantum states. These states determine their energy levels and how they move around the nucleus. The image at the top shows different possible states for an electron in a hydrogen atom.
- Light particles (photons): Light is made of tiny particles called photons. A photon's quantum state can describe its color (energy) and its polarization (how its electric field is oriented).
- Spin of a particle: Many particles, like electrons, have a property called "spin." It's like they're spinning, but it's not a physical spin like a top. The quantum state tells us if the spin is "up" or "down" or a mix of both.
Measuring a Quantum State
Measuring a quantum state is a bit tricky. In the quantum world, the act of measuring something can actually change its state. This is a key idea in quantum mechanics.
Imagine you want to know if a balloon is inflated or not. You can just look at it. But if you want to know the exact position of a tiny, super-fast particle, the light you use to "see" it might push it and change its position.
The Uncertainty Principle
A famous idea related to quantum states is the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. It says that you can't know certain pairs of properties about a particle with perfect accuracy at the same time.
For example, you can't know both the exact position and the exact momentum (speed and direction) of a particle at the same time. If you measure one very precisely, your knowledge of the other becomes less precise. The quantum state reflects this fundamental limit.
Why Quantum States are Important
Understanding quantum states is crucial for many modern technologies and scientific discoveries.
- Lasers: Lasers work because electrons in atoms are carefully controlled to be in specific quantum states.
- Computers: The tiny transistors in computer chips rely on the quantum behavior of electrons.
- MRI machines: Medical imaging like MRI uses the quantum spin of atomic nuclei to create detailed images of the inside of the body.
- Quantum computing: Scientists are trying to build new types of computers called quantum computers. These computers would use the special properties of quantum states to solve problems much faster than regular computers.
Quantum states help us understand the very fabric of reality at its smallest scales. They show us that the world of the tiny is much more complex and fascinating than our everyday experience suggests.
See also
 In Spanish: Estado cuántico para niños
In Spanish: Estado cuántico para niños

