Qwant facts for kids
 |
|
|
Type of site
|
Search engine |
|---|---|
| Available in | Multilingual |
| Headquarters | |
| Owner | Jean-Manuel Rozan, Éric Léandri, Patrick Constant, Caisse des dépôts et consignations (20%) Groupe Axel Springer (20%) |
| Founder(s) | Jean-Manuel Rozan, Éric Léandri, Patrick Constant |
| Commercial | Yes |
| Registration | None |
| Launched | July 2013 |
| Current status | Active |
|
Content license
|
Proprietary |
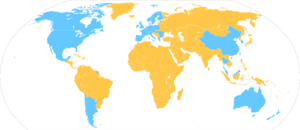
Qwant is a search engine from France. It started in February 2013. Qwant says it cares a lot about your privacy. This means it does not follow what you search for online. It also promises not to sell your personal information. Qwant also says it does not change search results to favor certain websites. Its search results are sometimes similar to the Microsoft Bing search engine. Qwant uses Bing when it needs more information or for image searches. Qwant is currently available in about 30 countries.
Contents
- What Does the Name Qwant Mean?
- How Qwant Started and Grew
- Different Versions of Qwant
- How Qwant Works
- How Qwant Makes Money
- Qwant's Partnerships
- How Qwant Uses Other Technologies
- What Qwant Can Do
- Qwant's Active Services
- Services Qwant No Longer Offers
- Who Uses Qwant?
- How Popular is Qwant?
- Qwant and Privacy
- See also
What Does the Name Qwant Mean?
The name Qwant comes from two parts. The "Q" is from the word "Quantum." The second part is from the English word "want."
How Qwant Started and Grew
The Beginning of Qwant
Qwant was created on May 25, 2011. It was started in Nice, France. The founders were Jean-Manuel Rozan, Éric Léandri, and Patrick Constant. Patrick Constant's company, Pertimm, had already made other search engines.
Qwant first launched a test version on February 16, 2013. It was available in 15 countries and 35 languages. The final version for France came out on July 4, 2013.
How Qwant Developed Over Time
When Qwant first started, it used a tool called an API from Microsoft Bing for its searches. An API helps different computer programs talk to each other. Qwant slowly started to use its own way of finding and organizing information, called "indexing." This process began in February 2013.
At first, Qwant did not have enough people or technology to do all its own indexing. They said they used their own system for social media and shopping results. But they still used outside APIs for other searches.
Until early 2019, Qwant mostly used Bing for web and image searches. This was because they did not have their own "crawler" or "indexer." A crawler is like a robot that explores the internet to find information.
In June 2014, a German company called Axel Springer SE invested money in Qwant. They helped Qwant develop a special robot to find news. This was to try and compete with Google News.
On April 14, 2015, Qwant showed a new look for its search engine. It had an updated design.
In October 2016, the European Investment Bank loaned Qwant €25 million. This money was to help Qwant grow more in Europe.
In February 2017, Qwant received €18.5 million more. Most of this money came from the Caisse des dépôts et consignations, a French financial group. They now own 20% of Qwant.
On July 4, 2018, Qwant launched a new, simpler version, called version four. Its logo also changed.
Changes and New Plans
In May 2019, Qwant announced it would move its computer servers. They moved some to a system called Microsoft Azure. They also kept some of their own indexing tools.
In January 2020, Jean-Claude Ghinozzi became the new CEO of Qwant.
By June 2020, Qwant started to reorganize. They closed some offices to meet the needs of their main investors.
In 2021, Raphaël Auphan and Corinne Lejbowicz took over managing Qwant. Their new plan was not to try and beat Google. Instead, they wanted to build a safe and private way to use the internet.
In early 2022, a new team started managing Qwant. Qwant stopped offering its services in some countries. It is still available in 39 countries around the world.
Working with Ecosia and Less Reliance on Microsoft
In 2023, Microsoft made its Bing search API much more expensive. Since Qwant used Bing for some searches, this change made Qwant rethink its business. Qwant then teamed up with Ecosia, a German search engine. They created a new company together called European Search Perspective (EUSP). Qwant shared its search indexing tools and some of its engineers. Ecosia contributed money.
Different Versions of Qwant
In June 2017, a version of Qwant for Switzerland was launched. It was available in German, French, and Italian.
In January 2018, Qwant planned to launch in China. This would be done with local partners to follow Chinese laws. The version launched in 2018, for Qwant's five-year anniversary, changed its look. It moved away from a column-based design to a more common web layout.
On December 3, 2019, Qwant announced a new design. This was to make it easier to use and add new features. In March 2021, another new version came out. It updated the look and made it better for smartphones.
In June 2022, Qwant showed a new look. This was to help more people, especially younger ones, understand why protecting personal data is important.
How Qwant Works
Qwant shows different types of results in one search. These include regular websites, shopping sites, and news. The results are not based on your past searches.
In 2016, Qwant said it was using more of its own search results. By 2020, Qwant claimed that over 50% of its web search results came from its own system. For all types of searches, it claimed 70% were independent.
How Qwant Makes Money
Qwant makes money partly from ads. These ads are shown based on what you search for, not on your personal information. Qwant also works with companies like Tripadvisor, PagesJaunes, and DeepL. For example, DeepL's translation service can appear directly on Qwant's results page. Qwant also uses tools from other companies like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube to improve its results.
Protecting Your Privacy
Qwant uses very few "cookies." Cookies are small files websites put on your computer. Qwant only uses them for the website to work, not for ads. It also saves your settings, like your favorite theme or language.
The search results you see are not changed based on your past searches. This is different from some other search engines like Google. Qwant's results depend on what is generally popular at the moment.
From mid-2016 to mid-2021, Qwant sent some data to Microsoft Bing Ads. This data included a part of your internet address (IP address), your browser type, and your search words. This data was changed so it couldn't be directly linked to you. Qwant did not tell its users about this until mid-2021.
Qwant's Partnerships
Working with Mozilla Firefox
On July 4, 2016, Qwant announced a partnership with the Mozilla Foundation. This led to a special version of the Firefox web browser that worked well with Qwant. A mobile version for phones came out on August 2, 2016. Qwant also released an app for Android and iOS phones. This app was based on a free and open-source version of Firefox.
Working with Inria
Qwant also partnered with Inria. Inria is a French research group. They worked together on internet search technologies that protect privacy.
Working with Phone Companies
- Wiko: On March 27, 2019, Qwant partnered with Wiko, a phone company. Wiko launched a new phone with Qwant as its main search engine. This was the first Android phone not to use Google as the default search engine.
- Fairphone: Qwant became the main search engine for the Fairphone 2 smartphone.
- Samsung: On May 12, 2020, Samsung Internet announced a partnership with Qwant. This meant Qwant would be available globally on Samsung's web browser.
- Huawei: Huawei chose Qwant as the main search engine for its P40 smartphone in France, Germany, and Italy. This happened because of rules from the US.
Other Partnerships
- Lexibook: In September 2018, Qwant and Lexibook worked together. They offered Qwant products, including Qwant Junior, on LexiTab tablets.
- Brave: Qwant became the main search engine for the Brave browser in France and Germany.
- Villes Internet: In August 2018, Qwant created Elunum. This was a search engine for local government officials.
- HelloAsso: On May 14, 2019, Qwant Causes was launched. It partnered with HelloAsso for handling donations.
- Qobuz: Qwant partnered with Qobuz, a music streaming service. This allowed users to listen to music recommended by Qwant in high quality.
- DeepL: Qwant launched a privacy-friendly translation service with DeepL. You can translate 28 languages directly from the Qwant search page.
How Qwant Uses Other Technologies
Xilopix
In November 2017, Qwant bought Xilopix. This company had its own search engine called Xaphir.
Nvidia
In April 2017, Qwant announced it would use Nvidia supercomputers. These powerful computers help Qwant improve its search results. Qwant also rented these computers to other new companies.
Fleksy
Qwant partnered with Fleksy. This allowed Qwant's search engine to be built into the Fleksy virtual keyboard.
Easyvoyage
Qwant worked with Easyvoyage, a travel comparison website. This helped Qwant provide results for flights and hotels.
Ecosia
In November 2024, Qwant and Ecosia announced a joint project. They are building the European Search Index. This new index will provide more local search results in French and German. It will also help them rely less on Bing and Google.
What Qwant Can Do
Searching for Information
With its new design in 2022, Qwant wants to teach people, especially younger ones, about protecting their personal data.
The main page has a section about keeping your digital information safe. There is also a search bar and links to other Qwant services like news.
When you search, Qwant tries to show direct answers or important information right away. There is also a simpler version called Qwant Lite.
Qwick Commands
Like some other search engines, Qwant lets you search directly on other websites. You do this by typing a special command called a Qwick.
Qwant's Active Services
Qwant Lite
On October 5, 2015, Qwant launched a simpler version called Qwant Lite. This version is for older computers or slow internet connections. It does not use complex web technologies, making it faster.
Qwant Junior
Qwant Junior is a special search engine for children aged 6–12. It has no ads, no online shopping, and no inappropriate content. Since 2018, it has been available on Android and iOS mobile devices.
It was first tested in French schools in January 2015. The final version came out in February 2015.
Since March 2023, Qwant Junior has partnered with the BayaM app. This app offers educational content for children.
Qwant Music
Qwant Music is a search engine for music. It helps you find albums and artists. It was made with Ircam and Qobuz.
The test version of Qwant Music launched on June 3, 2016. The final version came out on June 8, 2018.
Qwant VIPrivacy
Qwant VIPrivacy is a special tool for your web browser. It blocks trackers and cookies when you browse the internet. It also sets Qwant as your main search engine.
Qwant@Work
Launched in January 2023, Qwant@Work is for businesses and organizations. It helps protect employees' online privacy by limiting data collection. It also sets Qwant as the default search engine.
Services Qwant No Longer Offers
Masq by Qwant
Masq by Qwant was a service to store your personal data. It was meant to help Qwant personalize its service without collecting your information. It was stopped on September 17, 2020. Qwant said it "did not meet the expectations of most users."
Qwant Causes
Qwant Causes was a search engine that let you support projects while searching. It was similar to Ecosia. More ads were shown on search results pages to fund charities. This service was stopped on April 30, 2020, due to "insufficient use."
Qwant Boards
Qwant Boards allowed users to share images, videos, websites, or messages. On August 27, 2020, creating new boards and seeing others' boards was stopped. Qwant said this was to focus more on improving the main search engine.
Qwant Junior Education
This was a version of Qwant Junior for teachers in France. They could log in using their school email.
Qwant School
Qwant School was a filtered version of Qwant for teenagers, especially middle school students. Like Qwant Junior, it did not show ads or inappropriate content.
Qwant Maps
Qwant Maps was a mapping service. It was based on OpenStreetMap. It launched a test version on December 4, 2018. The final version came out in 2021.
Qwant Maps had features like finding directions (by car, foot, bike, or public transport) and places of interest. On May 20, 2024, Qwant announced it was stopping Qwant Maps. Instead, a "Maps module" is now part of the main search engine.
Qwant IoT
In May 2018, Qwant announced Qwant IoT. This was a search engine for "Internet of Things" devices.
QwantMed
QwantMed was a tool to protect private medical data.
Who Uses Qwant?
On October 2, 2018, Qwant became the main search engine for computers used by the French Ministry of armies.
On January 30, 2019, the company Safran started using Qwant as its main search engine.
In April 2019, the French space agency (CNES) decided to use Qwant. This included their launch site for rockets.
The French government announced that Qwant would be the main search engine on all its computers by April 30, 2020.
How Popular is Qwant?
In July 2013, a week after it launched, Qwant said it had 3.5 million visits each month.
By February 2016, it claimed 17.7 million monthly visits. In May 2016, it said it had one million visits, with half from France and 30% from Germany.
By the end of July 2017, Qwant claimed 40 million monthly visits. It was also reported that Qwant had 2% of the search market in France and 1% in Germany.
In June 2018, Qwant claimed to be the second most used search engine in France. It also said it was one of the top 50 most visited websites in France.
However, another website, StatCounter, showed different numbers. Between June 2017 and June 2018, StatCounter said Qwant was the fifth search engine in France. It had 0.55% of the market, while Google had 90.99%.
In 2018, Qwant said it handled 1.6 billion searches each month.
In April 2018, almost 81% of its users were from France. Germany was next with 5%, then Italy with 2%.
In the first half of 2020, Qwant was the fourth most popular search engine in France. It was behind Google, Bing, and Yahoo. It was ahead of Ecosia and DuckDuckGo.
In August 2020, 79% of its users were from France, 7% from Germany, and 3% from the United States.
As of February 2021, according to SimilarWeb, 51.78% of its users were from France. Other users came from the US (10.96%), Germany (9.23%), Canada (2.81%), and Italy (2.76%).
Qwant and Privacy
In September 2021, Qwant became available in all European countries. It also became one of the top 5 search engines available on Android phones. Qwant helped the European Commission make a rule in June 2021. This rule gives Android phone users more choices for their search engine.
On November 25, 2021, Qwant announced it helped create a "Manifesto of French startups." This document suggests ideas for digital privacy for the 2022 presidential election.
In January 2023, for Data Privacy Day, Qwant released its first online privacy report. It did this with other privacy-focused companies like Proton.
See also
 In Spanish: Qwant para niños
In Spanish: Qwant para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |