Rock dove facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Rock Pigeon |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Adult C. l. intermedia in India. | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Columba
|
| Species: |
C. livia
|
| Binomial name | |
| Columba livia Gmelin, 1789
|
|
 |
|
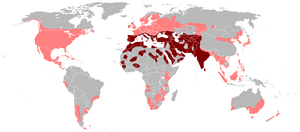
| Distribution | |
The rock pigeon (Columba livia), also known as the rock dove, is a common bird. It belongs to the bird family called Columbidae, which includes all doves and pigeons. Many people just call this bird a "pigeon."
Did you know that the domestic pigeons we see today came from this very species? When domestic pigeons escape, they become feral pigeons. These feral pigeons have spread all over the world.
Wild rock pigeons are usually pale grey. They have two black stripes on each wing. However, domestic and feral pigeons can come in many different colors and patterns. It's hard to tell males and females apart just by looking at them. Rock pigeons usually mate for life. They lay two young birds, called squabs, at a time. Both parents take care of their babies.
These birds live in open and partly open places. In the wild, they use cliffs and rocky ledges to rest and build their nests. Originally, rock pigeons lived in Europe, North Africa, and western Asia. Now, they live in cities all around the world. There are many of them, with millions of wild and feral birds in Europe alone.
Contents
What is a Rock Pigeon?
The rock pigeon was first described by a scientist named Johann Friedrich Gmelin in 1789. It is closely related to the hill pigeon. Other relatives include the snow pigeon, speckled pigeon, and white-collared pigeon.
This bird is also known as the "blue rock dove." For a while, its official name was "rock pigeon." But then, the International Ornithological Congress changed it back to "rock dove." Most people still just call it a "pigeon." Baby pigeons are called squabs.
How to Spot a Rock Pigeon

Adult rock pigeons are about 29 to 37 centimeters (11 to 15 inches) long. Their wings can spread from 62 to 72 centimeters (24 to 28 inches). Wild pigeons usually weigh between 238 and 380 grams (8 to 13 ounces). But pigeons that get a lot of food, like those in cities, can weigh more.
Their heads, necks, and chests are dark bluish-grey. Their neck and wing feathers have shiny colors like yellow, green, and purple. Their eyes are orange, red, or gold, with a lighter ring inside. The skin around their eyes is bluish-grey. Their beak is grey-black, with a noticeable off-white bump called a cere. Their feet are purplish-red.
Female pigeons look almost the same as males. But the shiny colors on their necks are not as bright.
The best way to tell a pure rock pigeon apart is its white lower back. They also have two black stripes on their pale grey wings. Their tail has a black band at the end. They fly fast and strong, especially when leaving sea caves.
Young pigeons are not as colorful or shiny. Their eyes are usually orange, but some can have white-grey eyes. Their eyelids are orange, surrounded by a grey-white ring. Their feet are red or pink.
When a pigeon flies overhead, you can see its white underwings. Its flight, behavior, and voice are typical of pigeons. They often glide, holding their wings in a V-shape. Pigeons visit fields to eat grains and green plants.
Pigeons look for food on the ground, either alone or in groups. They are scavengers, meaning they often eat human leftovers. In groups, some pigeons find food (producers), while others eat what the producers find (scroungers). Usually, there are more scroungers than producers in a group. Pigeons rest together in buildings, on walls, or on statues.
Most birds take small sips of water and tilt their heads back to swallow. But pigeons can drink continuously without tilting their heads. If a pigeon in a group gets scared, it will fly off with a loud clapping sound. This sound tells other pigeons in the flock to fly away too.
Pigeons, especially homing pigeons, are famous for finding their way home from far away. Even with this amazing skill, wild rock pigeons usually stay in their local areas.
Where Rock Pigeons Live
The rock pigeon naturally lives in western and southern Europe, North Africa, and parts of South Asia. During breeding season, they are often seen in pairs. But usually, they live in groups. This bird has spread widely across the world. There are an estimated 17 to 28 million of them in Europe alone.
Scientists believe rock pigeons first came from southern Asia. Old bones found in Israel show they have been there for at least 300,000 years. Because they have lived with humans for so long, it's hard to know exactly where they first came from.
Their natural home is on cliffs, often by the coast. Their domesticated form, the feral pigeon, has been introduced to many other places. Feral pigeons are very common, especially in cities, all over the world. A rock pigeon usually lives for 3 to 5 years in the wild. In captivity, they can live up to 15 years. The main reasons they die in the wild are predators and humans. Rock pigeons were first brought to North America in 1606.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Rock pigeons can breed any time of year. But they are most active in spring and summer. They build nests on coastal cliffs. They also use tall buildings with ledges or roof spaces, which are like artificial cliffs.
The nest is a simple platform made of straw and sticks. It is placed on a ledge, often on window ledges of buildings. The female lays two white eggs. Both parents take turns sitting on the eggs. This incubation period lasts 17 to 19 days.
When a squab (baby pigeon) hatches, it has pale yellow fuzz and a pink beak with a dark stripe. For the first few days, the parents feed the squabs "crop milk." This special milk is made in the parents' throats. All pigeons and doves produce it. The squabs leave the nest after about 30 days.
Pigeon Predators
Pigeons are a favorite meal for many birds of prey around the world. Because feral pigeons live in almost every city, they are a main food source for raptors that live in cities. Peregrine falcons and Eurasian sparrowhawks are natural hunters of pigeons. They are very good at catching and eating them. In some cities, up to 80% of a peregrine falcon's diet is feral pigeons.
Other common predators of feral pigeons in North America include opossums, raccoons, red-tailed hawks, great horned owls, and eastern screech owls. Birds that hunt pigeons can range from small American kestrels to large golden eagles. Even gulls, crows, and ravens might hunt them. On the ground, adult pigeons, their young, and their eggs are at risk from wild and pet cats. People also hunt some types of doves and pigeons for food.
Pigeons have fluffy feathers that are loosely attached to their skin. This means they can fall out easily. If a predator catches a pigeon, many feathers come off in the attacker's mouth. The pigeon might use this moment to escape. They also tend to drop their tail feathers when scared or caught. This is probably another way to distract a predator.
How Pigeons Keep Clean
Pigeons use special "powder down" feathers to clean themselves. These feathers break down into a fine powder, like talcum powder. This powder helps keep their feathers soft and silky. Pigeons do not have a preen gland, which most birds use to get oil for cleaning. So, they use this powder instead.
Some types of domestic pigeons have "fat quills." These feathers contain a yellow, oily fat. This fat comes from the same cells as the powder down. Pigeons use this oil when cleaning. It helps protect their feathers from bacteria.
Pigeons and Humans
Humans have kept rock pigeons as pets and for other uses for thousands of years. This has led to many different breeds of fancy pigeons. These come in all sizes, colors, and types. Domesticated pigeons are used as homing pigeons, for food, and as pets.
In the past, they were also used as carrier pigeons to send messages. Some pigeons, called war pigeons, played important roles in wars. Many pigeons have even received awards for their bravery. They saved hundreds of human lives. For example, a British pigeon named Cher Ami received a French medal for its actions in World War I. The Irish pigeon Paddy and the American pigeon G.I. Joe both received the Dickin Medal for their actions in World War II. Thirty-two pigeons have received this award.
Feral Pigeons
Many domestic pigeons have escaped or been set free over the years. These birds have become feral pigeons. They show many different feather patterns. But many still have the blue-barred pattern, just like the pure wild rock pigeon. Feral pigeons are found in large numbers in cities and towns all over the world. The pure wild rock pigeon is rare partly because it breeds with these feral birds.
Stages of a Pigeon's Life
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Paloma bravía para niños
In Spanish: Paloma bravía para niños
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |
























