Russian Far East facts for kids

The Russian Far East is a huge area in the eastern part of Russia. It stretches from Lake Baikal in Siberia all the way to the Pacific Ocean. This region is the easternmost part of Russia.
It shares land borders with Mongolia, China, and North Korea to the south. It also has sea borders with Japan to the southeast and the United States to the northeast. Even though it's close to Siberia, the Russian Far East is usually seen as its own separate region in Russia.
Contents
What is the Russian Far East?
The Russian Far East is a massive area, much larger than many countries. It covers about one-third of Russia's total land. This region is known for its wild nature, huge forests, and many volcanoes. It's a place of extreme weather, from very cold winters to warm summers.
Geography and Nature
The landscape here is very diverse. You can find high mountains, active volcanoes, and vast plains. There are also many rivers, like the Lena River and the Amur River, which are important for transport and trade. The coastlines are long, with many islands and bays.
Volcanoes and Earthquakes
The Kamchatka Peninsula in the Russian Far East is famous for its many volcanoes. Some of them are still active! This area is part of the "Ring of Fire," a zone around the Pacific Ocean where many earthquakes and volcanic eruptions happen. It's a very exciting place for scientists who study the Earth.
Climate and Seasons
The weather in the Russian Far East can be very different depending on where you are. In the north, it's extremely cold, with long, harsh winters. In the south, near the border with China, the climate is milder, with warm summers and cold, snowy winters. The region gets a lot of snow in winter, and some areas are covered in permafrost (ground that is always frozen).
Wildlife and Plants
This region is home to many unique animals and plants. Because it's so big and has different climates, you can find a wide variety of wildlife.
Amazing Animals
One of the most famous animals here is the Siberian tiger, the largest cat in the world. These tigers live in the forests of the Primorsky Krai region. Other animals include brown bears, wolves, lynx, and various types of deer. The coastal areas are home to seals, whales, and many seabirds.
Unique Plants
The forests are mostly made up of coniferous trees like fir, spruce, and larch. In some areas, especially in the south, you can find mixed forests with oak and maple trees. There are also many types of berries and mushrooms that grow wild.
People and Cities
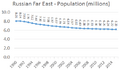
Even though the Russian Far East is huge, not many people live there compared to other parts of Russia. Most people live in cities along the rivers or the coast.
Main Cities
The two biggest cities are Vladivostok and Khabarovsk.
- Vladivostok is a major port city on the Pacific Ocean. It's an important center for trade and has a big naval base. It's also the end point of the famous Trans-Siberian Railway.
- Khabarovsk is another important city, located on the Amur River. It's a key administrative and cultural center for the region.
Life in the Cities
Cities like Vladivostok and Khabarovsk have modern buildings, universities, and cultural places like theaters and museums. Students in Vladivostok even celebrate Tatiana Day, which is also known as Russian Students Day. Life in these cities can be busy, just like in other big cities around the world.
History and Development
The Russian Far East has a rich history. For a long time, it was home to different indigenous (native) groups. In the 17th century, Russian explorers started to arrive. The region became part of the Russian Empire and later the Soviet Union.
Building the Region
Building up the Russian Far East was a big challenge because of its remote location and harsh climate. The Trans-Siberian Railway, completed in the early 20th century, was very important. It connected the region to the rest of Russia, making it easier to move people and goods. Many people, including some from Ukraine, moved to the region to help develop it.
Modern Challenges
Today, the Russian Far East is still developing. The government is trying to attract more people and businesses to the area. It's a region with a lot of natural resources, like minerals, oil, and gas, which are important for Russia's economy.
See also
 In Spanish: Extremo Oriente ruso para niños
In Spanish: Extremo Oriente ruso para niños
Images for kids
-
Vladivostok in the early 1900s
-
Number and share of Ukrainians in the population of the regions of the RSFSR (1926 census)
-
Students in Vladivostok celebrating St. Tatyana's Day, or Russian Students Day (2009)
-
Transportation on the Lena River (2004)