Rust Belt facts for kids
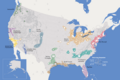
The Rust Belt is a part of the north central United States. It includes many states near the Great Lakes. This area was once famous for making steel and other heavy industrial products. But this type of work has greatly decreased since the mid-1900s. This happened partly because the United States started buying goods from factories in other countries.
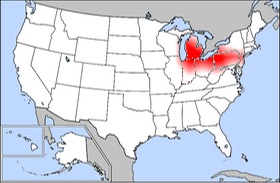
Many cities in the Rust Belt, like Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania and Youngstown, Ohio, have seen their population shrink a lot since the 1950s and 1960s.
Contents
What is the Rust Belt?
The name Rust Belt refers to a region in the United States. It's mostly found around the Great Lakes. This area was once a huge center for making things. It had many factories that produced steel and other heavy goods.
Over time, many of these factories closed down. This left behind old, rusting buildings and machines. That's how the area got its name, "Rust Belt."
Why Did Industry Decline?
For a long time, the Rust Belt was a very busy place. Factories here made cars, steel, and many other important products. But starting in the middle of the 20th century, things began to change.
Many companies started to move their factories. They built new ones in other countries. This was often because it was cheaper to make products there. When factories moved, many jobs were lost in the Rust Belt.
This change caused a lot of problems for the cities in the area. Fewer jobs meant fewer people living there.
Cities in the Rust Belt
Many cities in the Rust Belt have seen big changes. Their populations have become much smaller since the 1950s and 1960s.
Some well-known cities in the Rust Belt include:
- Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
- Erie, Pennsylvania
- Youngstown, Ohio
- Canton, Ohio
- Steubenville, Ohio
- Gary, Indiana
- Flint, Michigan
These cities are now working to bring new types of businesses and jobs to their areas. They are trying to rebuild and become strong again.
Images for kids
-
Allentown, Pennsylvania in the U.S. Rust Belt, May 2010
-
Deteriorating U.S. net international investment position (N.I.I.P.) has caused concern among economists over the effects of outsourcing and high U.S. trade deficits over the long-run.
-
The Bethlehem Steel plant in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania was one of the world's largest steel manufacturers for most of the 20th century. It suspended most of its operations in 1982 and declared bankruptcy in 2001. Its Bethlehem-based blast furnaces remain intact, but part of the property was sold in 2007 and turned into the Wind Creek Bethlehem resort and casino.
-
A disused grain elevator in Buffalo, New York
-
An abandoned Fisher auto body plant in Detroit
-
The Huber Breaker in Ashley, Pennsylvania was one of the largest anthracite coal breakers in North America. It was built in the 1930s and closed in the 1970s.
See also
 In Spanish: Rust Belt para niños
In Spanish: Rust Belt para niños