Samuda Brothers facts for kids
| Industry | |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1843 in Leamouth, London |
| Founders |
|
| Defunct | 1890s |
| Headquarters | Cubitt Town, Isle of Dogs,
,
United Kingdom
|
Samuda Brothers was a company in London, England, that built ships and did engineering work. It was located in Cubitt Town on the Isle of Dogs. Two brothers, Jacob Samuda and Joseph d'Aguilar Samuda, started the company. Today, the area where their shipyard once stood is called Samuda Estate.
Contents
Building Ships: Early Days and Challenges
The Samuda Brothers started their business in 1843. They rented a place on the Goodluck Hope peninsula in Leamouth, London, near the Bow Creek.
However, they faced a terrible accident with one of their first ships, the Gipsy Queen. In November 1844, during its test trip, something went wrong, and the ship was severely damaged. Sadly, Jacob Samuda and nine of the company's workers died in this incident. Another accident happened at their shipyard in 1845, which also resulted in the loss of three more workers.
After these difficult events, the company moved to Cubitt Town in 1852. Their old location was too small and surrounded by other businesses. By this time, Joseph was in charge of the company, as his brother Jacob had passed away.
The new shipyard in Cubitt Town became very good at building warships made of iron and steel, as well as fast steam ships. By 1863, it was said that Samuda Brothers was building twice as many ships as all the other shipyards in London combined!
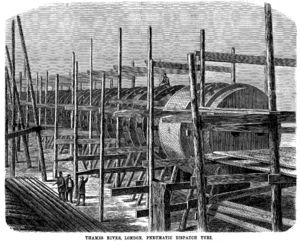
The company also made parts for a special train system called the Waterloo and Whitehall Railway. This was an atmospheric railway, which used air pressure to move trains. But the project was stopped because of a big money problem in 1866, known as the 1866 financial crisis. Many other London shipyards struggled during this time. Luckily, Samuda Brothers got orders from countries like Germany, Russia, and Japan, which helped them survive the crisis.
A Future Admiral Learns at Samuda Brothers
In 1877, a young man named Togo Heihachiro came to work at Samuda Brothers. He would later become a very famous Japanese admiral. Before coming to Samuda, he had studied at the Naval Preparatory School in Portsmouth and the Royal Naval College in Greenwich.
While at Samuda Brothers, Togo helped oversee the building of a ship called the Fusō. After his time there, he returned to Japan. Togo Heihachiro went on to lead the Imperial Japanese navy to a big victory in the Russo-Japanese War. This win helped Japan become a very strong country in the world.
The End of Samuda Brothers
Joseph Samuda passed away in 1885. After his death, people tried to sell the company so it could keep running. However, they were not successful. Because of this, Samuda Brothers closed down in the 1890s. This left Yarrows and Thames Ironworks as the last major shipbuilders in London.
Ships Built by Samuda Brothers
Samuda Brothers built many important ships during their time. Here are some of them:
- SS Carnatic (1862) for the P&O
- HMS Tamar (1863) for the Royal Navy
- BAP Independencia (1864) for the
 Peruvian Navy
Peruvian Navy - Mahroussa (1865) for the Khedive of Egypt
- Bordein (around 1865), a Nile steamer for the Khedive of Egypt
- SMS Kronprinz (1867) for the Prussian Navy
- Muin-i Zafer (1869) for the Ottoman Navy
- SMS Deutschland (1875) for the German Navy
- Fusō (1877) for the
 Imperial Japanese Navy
Imperial Japanese Navy - HMS Belleisle (1876) for the Royal Navy (was originally planned for the Ottoman Empire)
- HMS Orion (1879) for the Royal Navy (was originally planned for the Turkish Navy)
- ARA Almirante Brown (1880) for the Argentine Navy
- Riachuelo (1883) for the Brazilian Navy
- HMS Sappho (1891) for the Royal Navy
- PS Myleta (1891), a paddle steamer built for the South Eastern Railway. It was taken apart in 1909.
See also
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |