San Jacinto fault facts for kids
The San Jacinto Fault Zone is a series of giant cracks, called faults, that stretch across Southern California. Imagine them as long lines where the Earth's rocky plates meet and can sometimes slip past each other. This fault zone is often thought of as a "sister" to the much older and more famous San Andreas Fault. Some cities that sit right on top of or very close to this fault zone include San Bernardino, San Jacinto, and Hemet. If a large earthquake were to happen along this fault, it could have a big impact on the Greater Los Angeles area.
Contents
Understanding Faults and Earthquakes
What is a Fault?
A fault is basically a fracture or a break in the Earth's crust. Think of the Earth's surface as a giant jigsaw puzzle made of huge pieces called tectonic plates. These plates are always moving, but very slowly, usually only a few centimeters a year. When these plates push, pull, or slide past each other, stress builds up along the faults.
How Earthquakes Happen
When the stress along a fault becomes too great, the rocks on either side suddenly slip past each other. This sudden movement releases a lot of energy, which travels through the Earth as seismic waves. These waves are what we feel as an earthquake. The San Jacinto Fault Zone is known as a strike-slip fault. This means that the two sides of the fault move horizontally past each other, like two cars driving in opposite directions on parallel roads.
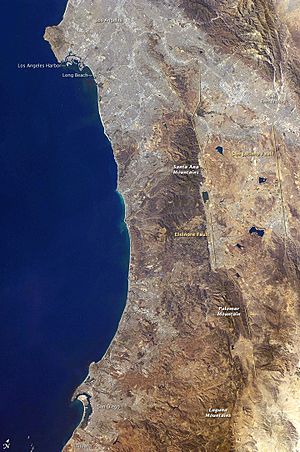
The San Jacinto Fault Zone's Location
The San Jacinto Fault Zone is one of the most active fault systems in California. It runs for about 200 miles (320 kilometers) through several counties, including Imperial, Riverside, San Bernardino, and San Diego. It's a key part of the larger San Andreas Fault system, which is the main boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate in California.
Cities Near the Fault
Many communities are located very close to the San Jacinto Fault Zone. Besides San Bernardino, San Jacinto, and Hemet, other areas like Palm Springs and parts of San Diego are also affected by its presence. Living near an active fault means that people in these areas need to be prepared for earthquakes.
Earthquake Activity and Risks
Past Earthquakes
The San Jacinto Fault Zone has a history of producing many earthquakes, including some strong ones. Scientists study these past events to understand how often earthquakes occur and how powerful they might be. For example, there have been several earthquakes with magnitudes greater than 6.0 on this fault over the last century.
Future Earthquake Risks
Because the San Jacinto Fault Zone is so active, scientists believe it has a high chance of producing another large earthquake in the future. Such an earthquake could cause significant shaking and damage to buildings and infrastructure, especially in nearby cities. This is why it's important for people living in Southern California to have earthquake preparedness plans, like securing furniture, having emergency kits, and knowing what to do during and after an earthquake.
Why Study the San Jacinto Fault?
Scientists, called geologists and seismologists, study faults like the San Jacinto Fault Zone to better understand how earthquakes work. By monitoring the fault's movements and studying its history, they can improve earthquake forecasts and help communities prepare. This research helps to make cities safer for everyone.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Zona de la Falla de San Jacinto para niños
In Spanish: Zona de la Falla de San Jacinto para niños