Schwerer Gustav facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Schwerer Gustav |
|
|---|---|
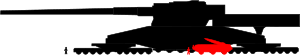
Schwerer Gustav (black) compared to an SS-21 SRBM launcher (red)
|
|
| Type | Super-Heavy Railway Gun |
| Place of origin | |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1941–1945 |
| Used by | Wehrmacht |
| Wars | World War II |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Krupp |
| Designed | 1934 |
| Manufacturer | Krupp |
| Unit cost | 7 million Reichsmark |
| Produced | 1941 |
| No. built | 2 |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 1,350 tonnes (1,490 short tons; 1,330 long tons) |
| Length | 47.3 metres (155 ft 2 in) |
| Barrel length | 32.5 metres (106 ft 8 in) L/40.6 |
| Width | 7.1 metres (23 ft 4 in) |
| Height | 11.6 metres (38 ft 1 in) |
| Crew | 250 to assemble the gun in 3 days (54 hours), 2,500 to lay track and dig embankments. 2 Flak battalions to protect the gun from air attack. |
|
|
|
| Caliber | 800 millimetres (31 in) |
| Elevation | Max of 48° |
| Rate of fire | 1 round every 30 to 45 minutes or typically 14 rounds a day |
| Muzzle velocity | 820 m/s (2,700 ft/s) (HE) 720 m/s (2,400 ft/s) (AP) |
| Effective firing range | about 39,000 metres (43,000 yd) |
| Maximum firing range | 48,000 metres (52,000 yd) (HE) 38,000 metres (42,000 yd) (AP) |
Schwerer Gustav (meaning Heavy Gustaf) and Dora were two giant World War II German guns. They were so big they had to be carried on railway tracks. These guns were designed to attack very strong enemy forts.
They were built in the late 1930s by a famous German company called Krupp. The guns were meant to destroy the powerful Maginot Line forts in France. Each gun weighed almost 1,350 tonnes, which is like 1,350 small cars! They could shoot huge shells that weighed seven tonnes (7,000 kg). These shells could fly as far as 37 kilometers (about 23 miles).
Contents
Gustav and Dora in World War II
The Schwerer Gustav and Dora guns were not ready when World War II started. The German army, called the Wehrmacht, went around the Maginot Line by going through Belgium. This meant the guns were not needed for their first planned mission.
Gustav's Role in Sevastopol
However, the guns were ready by autumn 1941. This was after the Wehrmacht invaded the Soviet Union in an attack called Operation Barbarossa. Gustav was used during the siege of Sevastopol in the summer of 1942. A siege is when an army surrounds a city to try and capture it.
By July 4, 1942, the city of Sevastopol was completely ruined. About 30,000 tonnes of artillery ammunition had been fired. Gustav alone fired 48 huge shells. Its original barrel wore out because it had already fired about 250 shells during testing. The gun then got a new barrel, and the old one was sent back to the Krupp factory to be fixed.
The End of the Giant Guns
Both Gustav and Dora were later moved to Leningrad. They might have been planned for use in Warsaw too. In the end, Gustav was captured by American soldiers and taken apart. Dora was destroyed by the Germans near the end of the war. They did this to stop the Red Army (the Soviet army) from capturing it.
The Largest Rifled Weapon
The Schwerer Gustav was the largest gun with a rifled barrel ever used in a real battle. A rifled barrel has grooves inside that make the shell spin, helping it fly straight. It also fired the heaviest shells of any artillery gun. There were a few other very large guns built, but they were never used in combat. These included the French Monster Mortar and the British Mallet's Mortar.
Images for kids
-
An 800 mm Schwerer Gustav shell at the Imperial War Museum, London
-
A shell for the Dora gun (without the sharp ballistic cap) found after the war at the former German firing range near Rügenwalde (today Darłowo), on exhibition in the Polish Army museum in Warsaw
See also
 In Spanish: Cañón K (E) Schwerer Gustav para niños
In Spanish: Cañón K (E) Schwerer Gustav para niños






