Operation Barbarossa facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Operation Barabarossa |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Eastern Front of World War II | |||||||
 |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| ~3 million 3,600 tanks, 4,389 aircraft 46,000 artillery pieces |
~5.7 million 12,000-15,000 tanks, 35,000-40,000 aircraft (11,357 combat ready on 22 June 1941) |
||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 186,452 killed 40,157 missing 655,179 hurt 2,827 aircraft destroyed 2,735 tanks destroyed |
802,191 killed 1,336,147 hurt 2,835,000 captured. 21,200 aircraft destroyed 20,500 tanks lost |
||||||
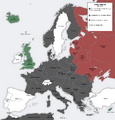
Operation Barbarossa (German: Unternehmen Barbarossa) was the secret name for the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and its allies during World War II. It began on June 22, 1941. The name came from Frederick I, a famous German emperor.
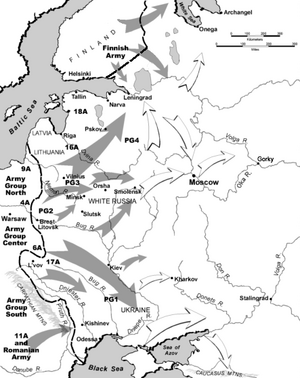
This invasion was the biggest military attack in human history. More than 3 million soldiers attacked along a front that was 2,900 kilometers (about 1,800 miles) long. They used 600,000 motor vehicles and 750,000 horses. The main goal was to quickly defeat the Soviet military. Germany also wanted to take control of the Soviet Union's rich natural resources. These resources would help Germany continue fighting the war against the Allied powers.
Even though the Soviet Union was not fully prepared, the German attack did not fully succeed. Germany did manage to take over important areas, especially in Ukraine. However, they were stopped near Moscow, the Soviet capital. After this, Germany could not launch another attack as large as Operation Barbarossa on the Eastern Front.
Contents
The Invasion Begins
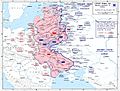
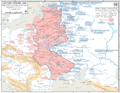
Operation Barbarossa was planned to start earlier, but it was delayed. When it finally began, it opened the Eastern Front of World War II. In Russia, this part of the war is called the Great Patriotic War.
The German army used a tactic called Blitzkrieg, which means "lightning war." This involved fast, powerful attacks using tanks and planes to quickly break through enemy lines. The goal was to surround and destroy large parts of the Soviet army very quickly.
Challenges for the Invaders
The German army faced many challenges during the invasion. One big problem was the harsh Russian winter. The winter of 1941-42 started early and was very cold. German soldiers were not ready for such extreme temperatures. Many were still wearing summer uniforms. They tried to stay warm by stuffing newspapers into their clothes.
The extreme cold also caused German equipment to break down. Tanks and vehicles struggled to operate in the freezing conditions. Many German soldiers suffered from frostbite or froze to death.
Soviet Resistance and Counterattack
Despite heavy losses, the Soviet Union fought back fiercely. The Soviet army, known as the Red Army, slowly pushed the German soldiers out of their country. This was a very costly fight for the Soviets. Around five times more Russians died than Germans during the entire Eastern Front conflict.
After pushing the Germans out of Russia, the Soviets launched their own attacks into German-controlled areas in Eastern Europe. Eventually, they invaded Germany itself. This led to the Battle of Berlin, which was the final major battle before Germany surrendered in 1945.
Impact of Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the largest military operation in history. It involved more soldiers and caused more deaths than any other single operation. It created a huge battleground where millions of people fought and died.
The failure of Operation Barbarossa was a major turning point in World War II. It forced Germany to fight a long, difficult war on two main fronts: the Eastern Front against the Soviet Union and the Western Front against the Western Allies. This split of forces weakened Germany and eventually led to its defeat.
Images for kids
-
Heinrich Himmler, Rudolf Hess, and Reinhard Heydrich listening to Konrad Meyer at a Generalplan Ost exhibition, 20 March 1941
-
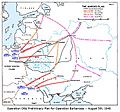
The Marcks Plan was the original German plan of attack for Operation Barbarossa, as depicted in a US Government study (March 1955).
-
OKH commander Field Marshal Walther von Brauchitsch and Hitler study maps during the early days of Hitler's Russian Campaign
-
Semyon Timoshenko and Georgy Zhukov in 1940
-
German forces pushing through Latvia, summer 1941
-
General Ewald von Kleist (left), commander of the 1st Panzer Group, inspects a large iron works facility in Ukraine, 1941
-
German general Heinz Guderian (centre), commander of Panzer Group 2, on 20 August 1941
-
Germans battle Soviet defenders on the streets of Kharkov, 25 October 1941
-
Soviet Ilyushin Il-2s flying over German positions near Moscow
See also
 In Spanish: Operación Barbarroja para niños
In Spanish: Operación Barbarroja para niños
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |