Libyan civil war (2014–2020) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Second Libyan Civil War |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Arab Winter, Libyan Crisis, Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict, War on terror, and Qatar–Saudi Arabia diplomatic conflict | |||||||
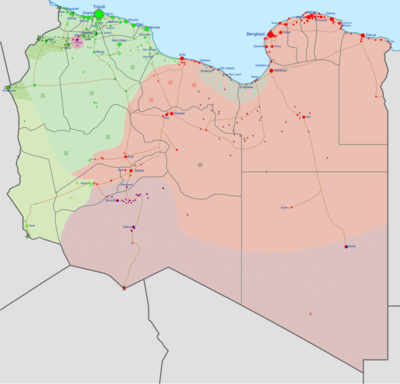 Military situation in Libya on 11 June 2020 Under the control of the House of Representatives and the Libyan National Army (LNA) Under the control of the Government of National Accord (GNA) and different militias forming the Libya Shield Force Controlled by local forces (For a more detailed map, see military situation in the Libyan Civil War)
|
|||||||
|
|||||||
The Second Libyan Civil War was a big conflict in Libya that lasted for six years. It started in 2014 and ended in 2020. Many armed groups fought each other. The main groups were the House of Representatives (HoR) and the Government of National Accord (GNA).
Contents
Understanding the Conflict
This war began after the 2011 Libyan Civil War. It was mainly a fight between two big groups. One was the House of Representatives (HoR). This group was based in eastern and central Libya. It had the support of the Libyan National Army (LNA). Countries like Egypt and the UAE also helped the HoR with airstrikes.
The other main group was the General National Congress (GNC). This group was based in western Libya. It was supported by different armed groups. Countries like Qatar and Turkey also gave some help to the GNC.
Why the Fighting Started
The conflict started because of disagreements over elections in 2014. The GNC first accepted the election results. But then they changed their mind. This happened after a court canceled a change about Libya's future plans.
The HoR refused to take power in Tripoli. Tripoli was controlled by armed groups. So, the HoR set up its own parliament in Tobruk. This city was controlled by General Haftar's forces.
Efforts for Peace
In December 2015, a peace deal was signed. It was called the Libyan Political Agreement. This agreement was made after long talks. Different political groups from Tripoli, Tobruk, and other places joined in. They agreed to form a new government. This new government was called the Government of National Accord (GNA). It was recognized by many countries around the world.
On March 30, 2016, Fayez Sarraj became the head of the GNA. He started working from Tripoli. Some groups, like the GNC, did not agree with this.
Other Groups Involved
Besides the main two groups, other armed groups also fought.
- The Shura Council of Benghazi Revolutionaries was an Islamist group. It was defeated in Benghazi in 2017.
- The Islamic State (ISIL) also had groups in Libya.
- The Shura Council of Mujahideen in Derna fought ISIL in Derna. Later, this group was also defeated.
- Many other armed groups and militias were involved. Their loyalties often changed.
Fighting Against ISIL
In May 2016, the GNA and GNC worked together. They launched an attack to take back areas from ISIL. This attack happened in and around Sirte. Because of this, ISIL lost control of all the important areas it held in Libya.
Later in 2016, some forces tried to overthrow the GNA. This attempt was led by Khalifa al-Ghawil.
The Tripoli Offensive
On April 4, 2019, Khalifa Haftar ordered his army to attack Tripoli. Haftar was the commander of the Libyan National Army. Tripoli was the capital of the GNA. The United Nations and its Secretary General, António Guterres, did not approve of this attack.
End of the Conflict
On October 23, 2020, a "permanent ceasefire agreement" was reached. This agreement was made by military groups from both sides. It meant that all foreign fighters had to leave Libya within three months. Also, a joint police force would patrol areas where there had been fighting.
On the same day, the first commercial flight between Tripoli and Benghazi took place. This was a sign of peace returning.
On March 10, 2021, a new government was formed. It was called the unity government. This government was supposed to stay in power until new elections. However, the elections have been delayed several times. This has caused new tensions.
Images for kids
-
General Khalifa Haftar
See also
 In Spanish: Segunda guerra civil libia para niños
In Spanish: Segunda guerra civil libia para niños
- 2022 Tripoli clashes
- 2020 Turkish intervention in Libya
- American intervention in Libya (2015–2019)
- European migrant crisis
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |






