Sexual dimorphism facts for kids


Sexual dimorphism is a term in biology. It means that the male and female of a species look different from each other. The word comes from Greek words: di (meaning two) and morphe (meaning form).
This difference between sexes is very common in nature. It often happens because of sexual selection. This is when animals compete to find a partner and reproduce. These differences are usually inherited, meaning they are passed down from parents to their offspring. They help males and females survive and have babies.
The features that make the two sexes look different are called secondary sex characteristics. These are not directly part of the reproductive system. Instead, they are traits that help an individual win against rivals when trying to find a mate.
Contents
How Males and Females Can Look Different
The differences between males and females can show up in many ways:
Size Differences
In some species, males are much larger than females. This often happens when males control a group of females, like gorillas or lions.
- For example, in tiny creatures called rotifers, males are always much smaller than females.
- Even more extreme are sea devil fish. Their tiny males actually attach themselves to the females and become part of them!
Special Features for Courtship
Sometimes, one sex has extra features used to attract a mate:
- Hair: Males often have more hair. Think of a male Gorilla with its big crest of hair.
- Teeth: In Asian elephants, only the males have tusks. Both male and female African elephants have tusks. Male pigs and walrusses have very large canine teeth.
- Horns or Antlers: These are often found only on males, like in deer.
Colouring Differences
Differences in colour are common, especially in butterflies.
- Sometimes, females use Batesian mimicry to look like dangerous animals, while males keep their usual colours.
- This helps females, who carry precious eggs, stay safe from predators.
- Males, however, need to be easily recognized by females for mating, so they often show off their true colours.
Why Sexual Dimorphism is Important
The main reasons for these differences are to help animals find a mate and reproduce:
Finding a Mate
Often, males will display their features, and females will choose the best mate. This is called mate selection.
Protecting Territory
Males might use their special features to show other males that they "own" an area. This helps them protect their space and resources.
Fighting for Mates
If males have "weapons" like horns or large teeth, they might use them to fight other males for the right to mate. These features also help them defend against predators.
When Differences Appear
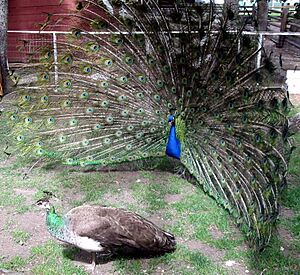
Some animals only show these differences during mating season. For example, deer grow antlers only at certain times of the year, and peacocks shed their long tail feathers when it's not mating season. This helps them avoid predators when they don't need to attract a mate, as being very showy can make them easier to spot.
Images for kids
-
Mandarin ducks, male (left) and female (right), showing how different their feathers are.
-
Male (bottom) and female mallards. The male mallard has a bright green head when it's time to find a mate.
-
Orgyia antiqua male (left) and female (right).
-
Some birds, like this mute swan, don't have different coloured feathers. You can tell them apart by their size or how they act. Male Mute swans (cobs) are usually taller and larger than females (pens). They also have thicker necks and a bigger "knob" above their beak.
-
Skeletons of female (left) and Male (right) black-casqued hornbills (Ceratogymna atrata). You can see the difference in the casque (a helmet-like growth) on top of their bills. These skeletons are at the Museum of Osteology.
-
Female triplewart seadevil (an anglerfish), with a tiny male attached near her vent (arrow).
-
Sexual dimorphism in ancient Cambrian trilobites.
-
Male (left), offspring, and female (right) Sumatran orangutans.
See also
 In Spanish: Dimorfismo sexual para niños
In Spanish: Dimorfismo sexual para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |